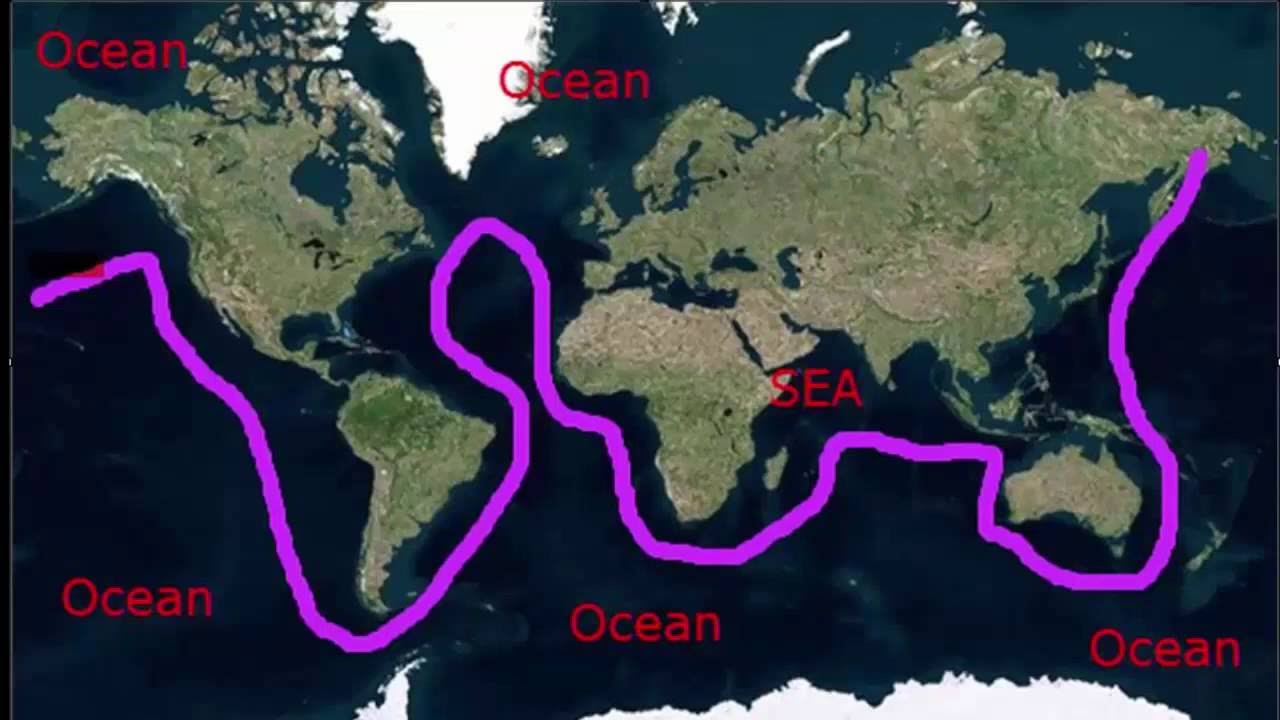
Overall, seas are smaller and partially.
What is the difference between sea and ocean. Sea has a direct outlet to the ocean, whereas, lakes do not. A lake is enclosed on all sides by land and does not connect to a larger water body like an ocean, while a sea connects. An ocean is a saltwater body that is larger in size than the sea.
Technically speaking, the term “sea” is used to describe smaller bodies of water, while the term “oceans” is used to describe larger bodies of water. Sea water is saltier than ocean water. The ocean is a large mass of salt water when compared to its size, they can either exist as part of the open ocean or as landlocked areas.
Although there are no major differences between a sea and an ocean, a sea is an extension of the ocean partly or wholly covering surrounding the land. The major differences between a lake and a sea are; They are big and not surrounded by any boundaries.
An ocean is a vast body of water whereas a sea is a comparatively small and partially confined body of water surrounded by land. The major difference between ocean and sea water is that oceans are very large bodies of water that cover a major portion of the earth while seas are smaller bodies of water that are found in. Most commonly, it means a large expanse of saline water connected with an ocean and is commonly used as a synonym for ocean.
The main difference between the two is their size, the seas are smaller than the oceans. This isn’t the only difference when. Oceans are enormous when compared to any sea.
Oceans are water bodies that cover 70% of the earth's surface. Lakes may be above or below sea level. In addition, the seas are closed, located.









![Map of all different seas and oceans [6240x3520] MapPorn](https://i2.wp.com/external-preview.redd.it/EO9lxBriU9eOeAJEd3ldQHScrlufV7XP6P2C8M8VfaU.png?auto=webp&s=b7cbc0c22b7012e5905cb2c91cbad6d97dcb36d3)