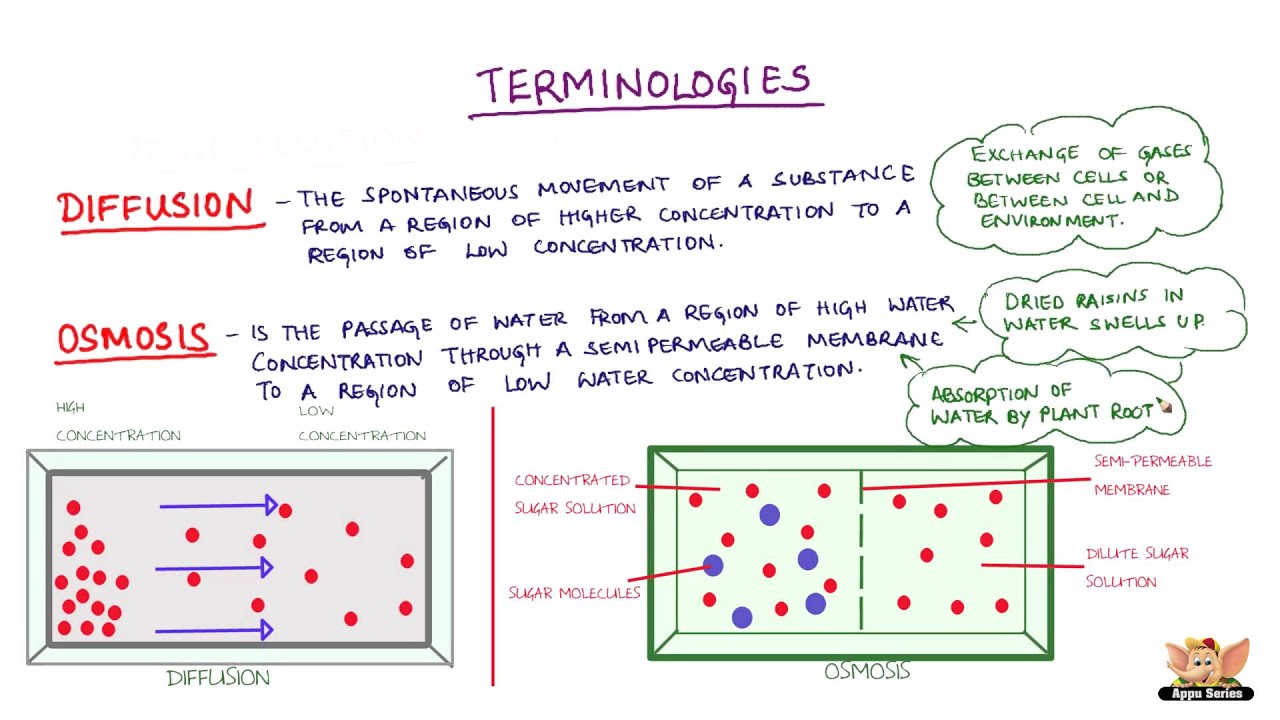
Osmosis refers to the process of movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane, from the solution of low concentration to the solution of high concentration.
What is osmosis simple definition. Noun absorption , assimilation , diffusion , engulfment , infiltration , ingress , interpenetration , introgression , passage , penetration , permeation. Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules from solution of low concentration to solution of high concentration, through a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules, from a region where the water molecules are in higher concentration, to a region where they are in lower concentration, through a partially.
Osmosis is when a substance crosses a semipermeable membrane in order to balance the concentrations of another substance. Movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of higher solute concentration that tends to equalize the concentrations of solute. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules down a water potential gradient, through a semipermeable membrane (also termed a partially permeable membrane).
In simple words, osmosis is the movement of water through a special mixture of solutes like salt particles within the solvent. If one side has a high concentration of solutes, there must be less water. What is osmosis in biology simple definition?
In biology, this is usually when a solvent. In osmosis, water moves from an area of higher.









