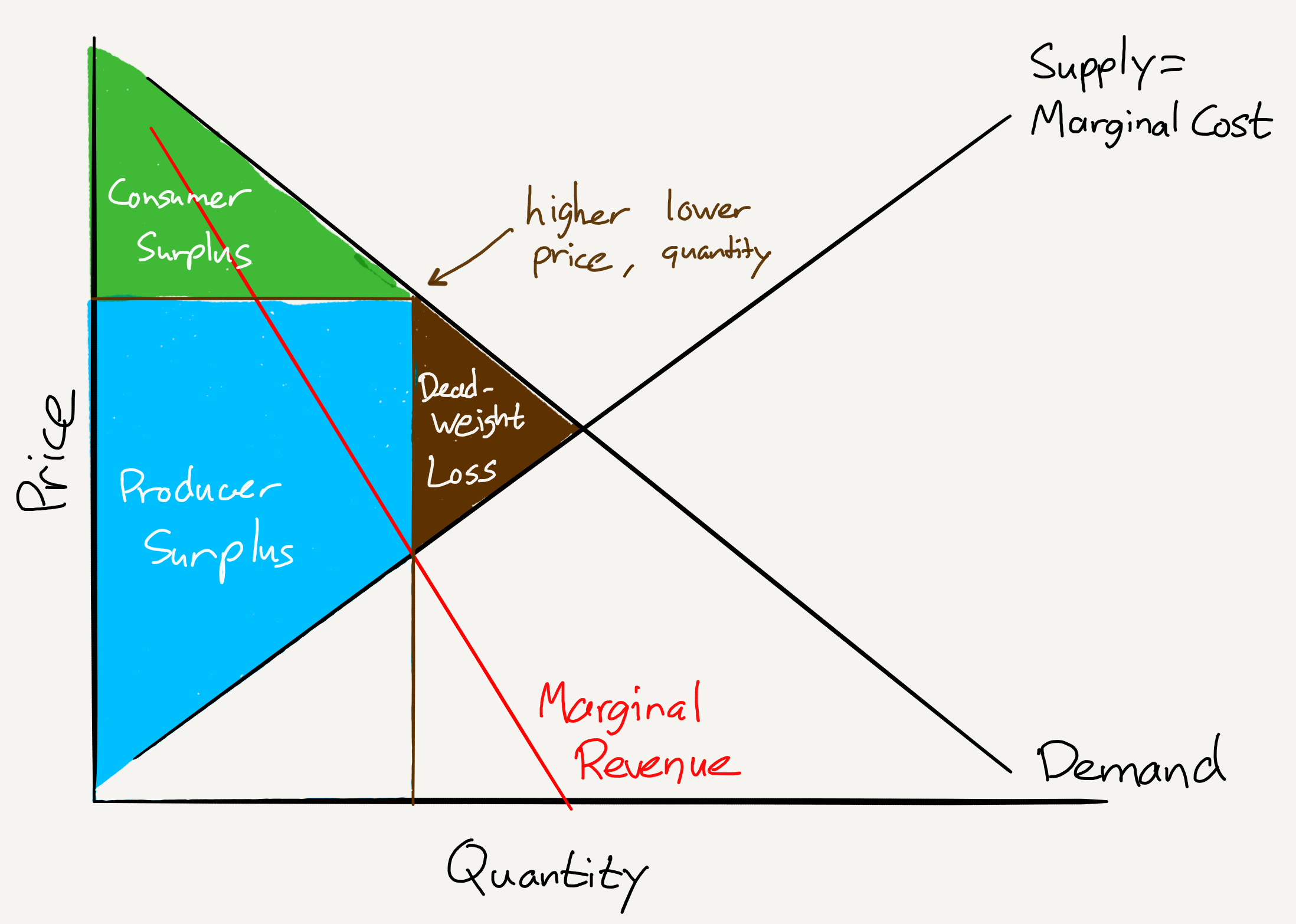
Since monopolies are inefficient they also have dead weight.
What is deadweight loss in a monopoly. The presence of deadweight loss is most commontly identified when the quantity produced relative to the amount consumed differs in regards to the optimal concentration of surplus. Mainly used in economics, deadweight loss. A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market.
The deadweight loss is the potential gains that did not go to the producer or the consumer. Notice that monopolies charge a higher price and produce a lower output than perfectly competitive markets. It is the loss of economic efficiency in terms of utility for consumers/producers such that the optimal or allocative efficiency is not achieved.
A deadweight loss is a loss in economic efficiency as a result of disequilibrium of supply and demand. The monopolist, on the other hand, will lose if competition is increased. The monopoly pricing creates a deadweight loss because the firm forgoes transactions with the consumers.
The deadweight loss is c + e. This difference in the amount reflects the quantity that is not being. In other words, society, particularly the consumers, loses utility:
In other words, goods and services are either being under or oversupplied. Jeff deadweight loss, economics, externalities, monopoly, deadweight loss is something that occurs in the economy when total society welfare is not maximized. The deadweight loss is the potential gains that did not go to the producer or the.
As a result of the deadweight loss, the combined surplus (wealth) of the monopoly. Consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum price. A deadweight loss is a cost to society created by market inefficiency, which occurs when supply and demand are out of equilibrium.









