The effect is photochemical not thermal.
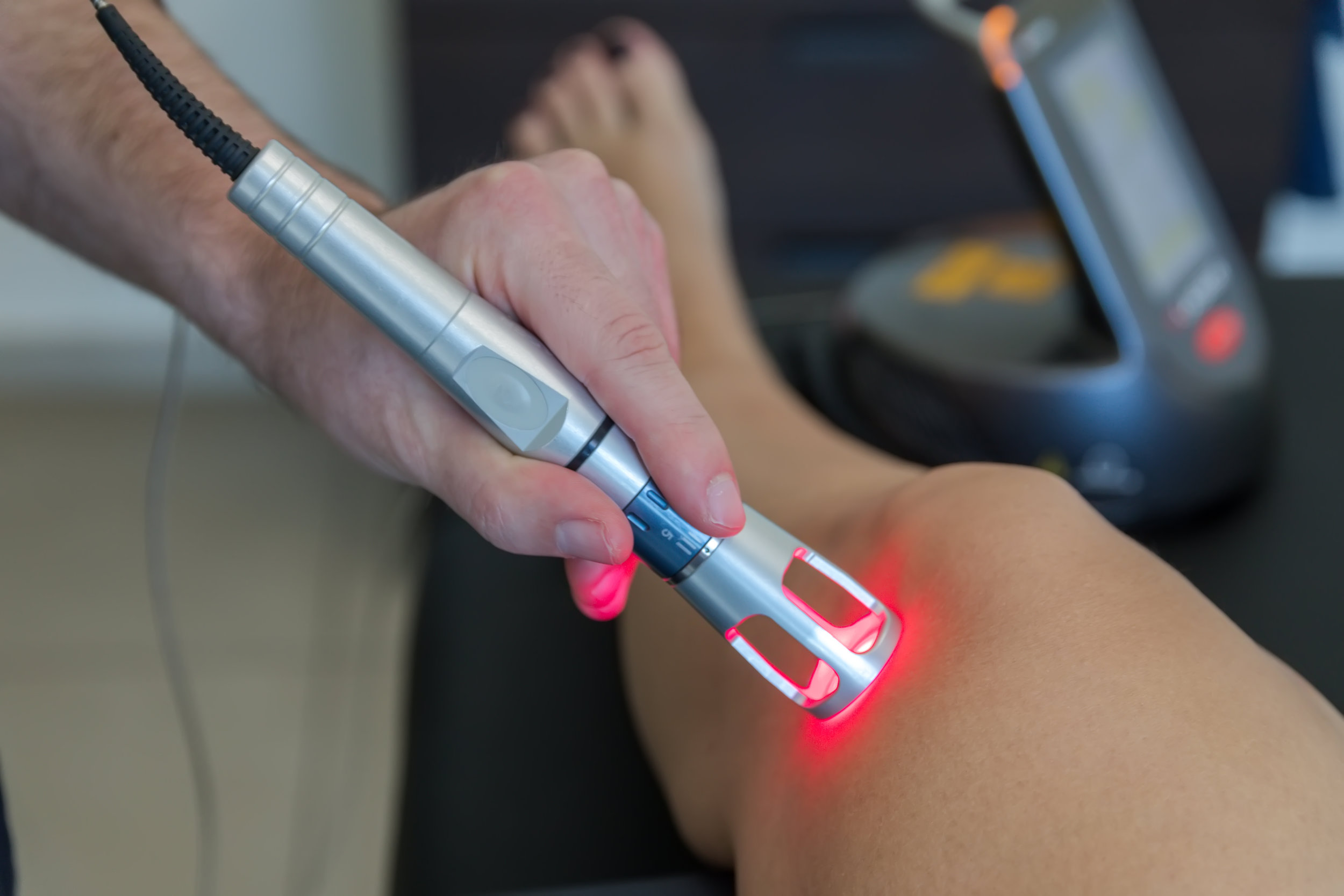
Low level laser therapie. Lllt dosage varied according to the anatomical location treated and was based upon guidelines developed by walt. Photons are absorbed by cellular photoreceptors, triggering chemical alterations and potential biochemical benefits to the human body. This type of laser differs from the one used for surgical interventions, in the sense that it does not generate any heat.
Low level laser therapy (lllt) is used by some physiotherapists to treat various musculoskeletal condition. 115 low power or cold lasers usually between 5 and 500 mw 115 have a nonthermal stimulatory effect on the tissues impacting cellular change. Cells then harness this energy and convert it into more atp.
It is also called photobiology or biostimulation. 1 count (pack of 1) 3.8 out of 5 stars. Low level laser therapy (lllt) sometimes known as low level light therapy or photobiomodulation (pbm) is a low intensity light therapy.
Laser hair therapy uses something called low level laser light therapy (lllt) to stimulate cellular activity in the hair follicles to slow down and minimize hair loss, while also supporting regrowth. Computerized searches (root up to feb 2012) included pain, function/disability, quality of life (qol) and global perceived effect (gpe). This allows the cells to inhibit pain and inflamation, then it enhances repair and regeneration of damaged cells.
Low level laser therapy (also called cold laser and class 3 laser) works by infusing the cells with energy; Hairmax ® specializes in treating hair loss with technology and specially formulated products. The effects appear to be limited to a specified set of wavelengths, and.
Low level laser therapy (lllt) has demonstrated the ability to significantly accelerate and enhance the body’s natural defense and repair mechanisms in the presence of injury, sports and workout injuries, inflammation and with certain disease processes. Of 17 trials, 10 demonstrated high. The light triggers biochemical changes within cells and can be compared to the process of photosynthesis in plants, where the photons are absorbed by cellular photoreceptors and.



















