Follow answered jan 28, 2016 at 2:20.
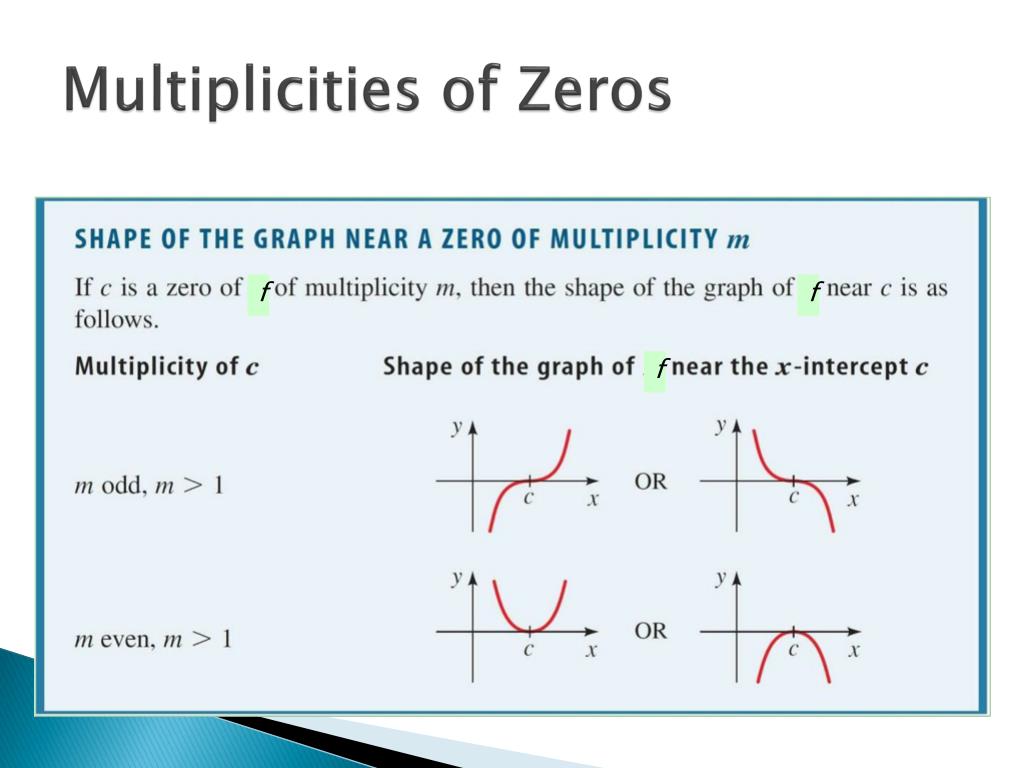
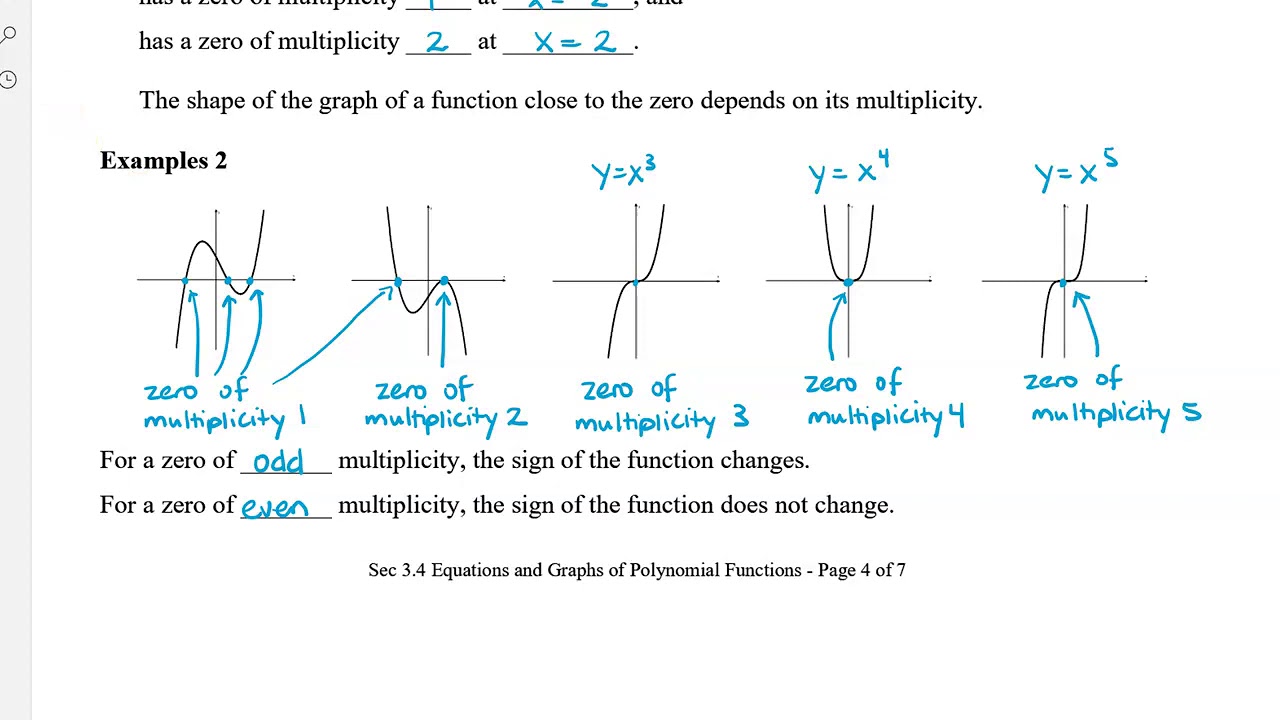
How to determine the multiplicity of a zero. In other words, the multiplicities are the powers. Find each zero by setting each factor equal to zero and solving the resulting equation. Find the multiplicity of each factor by examining the exponent on.
+ k, where a, b, and k are constants an. 0] polynomials have the property that if r is a zero of the polynomial p (x), then p (x) is divisible by x−r. When a linear factor occurs multiple times in the factorization of a polynomial, that gives the related zero multiplicity.
(for the factor x − 5, the. 👉 learn how to find all the zeros of a polynomial. Identify the zeros and their multiplicities.
For example, the quadratic ( x + 2) ( x − 3) has the roots x = − 2 and. 👉 learn about zeros and multiplicity. How many times a particular number is a zero for a given polynomial.
Multiplicity of zeros of polynomials. This function has a degree of four. What is 'zero of multiplicity'?
A zero or a root has a multiplicity, which refers to the number of times its associated factor appears in the polynomial. Multiplicity of zeros of polynomials. For more general functions, evaluate `f^(k)(x_0)` until it is zero.