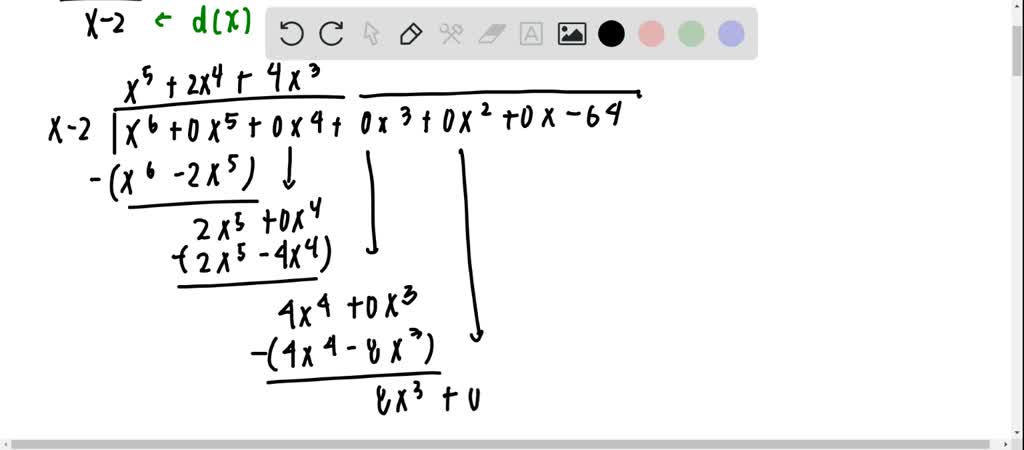
You can find the remainder and quotient with a polynomial.
What is the quotient in long division. Use the acronym dmsb, which stands for: Here’s a trick to mastering long division. Multiply 5 by 32 and write the answer under 167.
We get the quotient as 5, and the remainder as 0, as 3 x 5 = 15. In other words, it is the solution to the question how many times does a number (the divisor) go into another (the dividend )? a. Following are the two methods can be used to find the quotient when dividing polynomials.
I am sorry i cannot draw the math notation here. Consider 13 divided by 5. We learn how to do long division with polynomials, when some of the coefficients are equal to zero, 0.
Put the 5 on top of the division bar, to the right of the 1. The long division rules are explained in 12 steps for a case in which the dividend is a 3 length number, while the divisor is a 2 length one: Division is a method of distributing objects equally in groups and it is denoted by a mathematical symbol (÷).
So 6 times 6 is 36. Division using partial quotients is the new method for long division that's been taught in schools for the last 10 years or so. Now divide 26 by 4.
The quotient formula is given as follows: 8 minus 6 is 2. Here we are going to see some practice questions on finding quotient and remainder using long division.









