Quadratic functions in standard form.
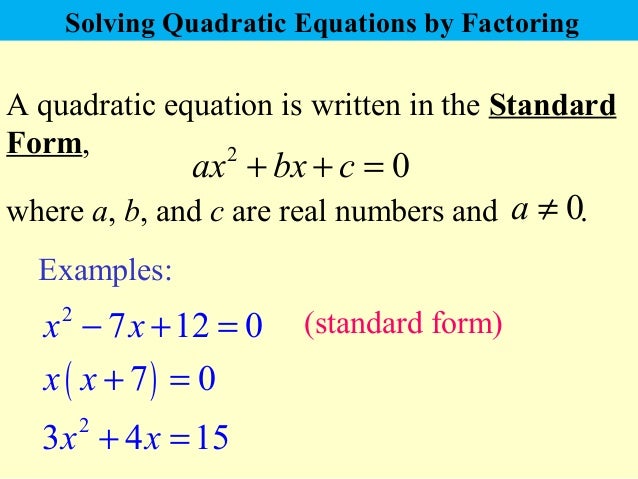
What is quadratic equation in standard form. Where a, b and c are real numbers, and a ≠ 0. Every quadratic equation can be written as ax 2 + bx + c = 0, which is called the standard form. The quadratic equation in its standard form is ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a and b are the coefficients, x is the variable, and.
This video contains plenty of examp. Therefore, the standard form of the quadratic equation is y=2x^2+28x+88. This algebra video tutorial explains how to write the quadratic equation in standard form given 2 solutions or 3 points.
In order to solve a quadratic equation, it is possible to add the same number to. Using vertex form to derive standard form. A quadratic equation is an algebraic equation of the second degree in x.
Ax2 + bx + c = 0 a x 2 + b x + c = 0. What is the standard form of the quadratic equation :n− n7=4. It has the one unknown value which is x and the a,b,c coefficients which have their own known value.
Where x represents an unknown, and a, b,. In writing quadratic equation in standard form, we use the format where.examples of quadratic equation in standard form are the following: The standard form is ax² + bx + c = 0 with a, b and.
If p (x) is a quadratic polynomial, then p (x) = 0 is called a quadratic equation. The standard form of a quadratic function is y = ax 2 + bx + c. You may also see the standard form called a.









