A common osmosis example seen in real life is the preservation of food.
What is osmosis. Food is preserved in salt or sugar solution (hypertonic) to allow water to be pulled out. The absorption of water by plant roots from the soil. Raisins when kept in water swell up.
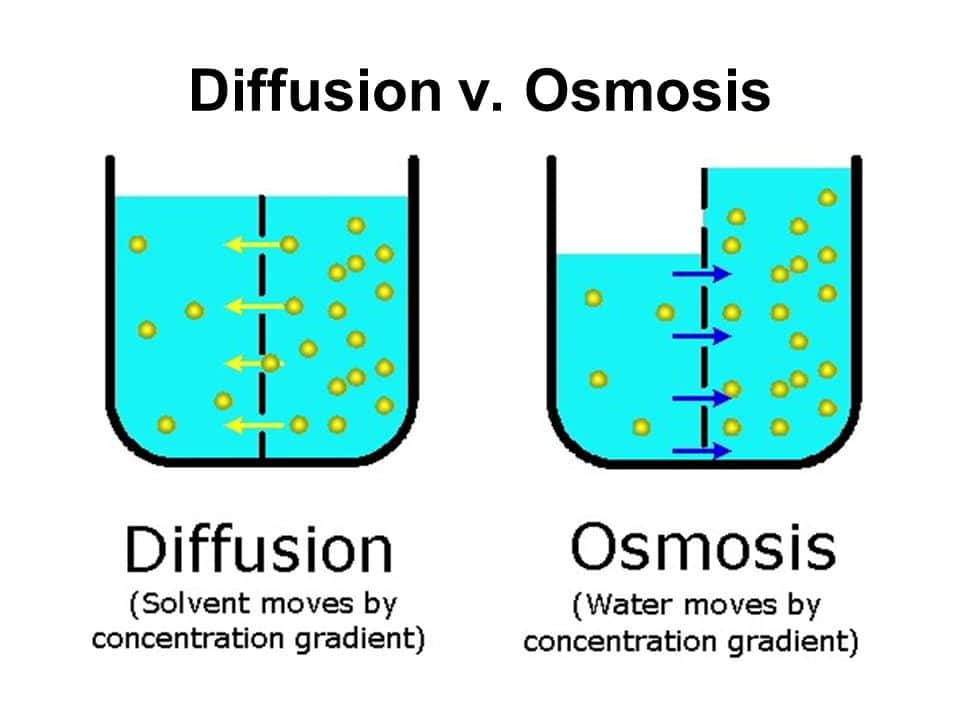
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute. The process named osmosis is the reason why the water from the surrounding medium enters the cells. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules down a water potential gradient, through a semipermeable membrane.
Learn and reinforce your understanding of osmosis. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Diffusion is when molecules or atoms move from an area of high concentration to an.
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules from solution of low concentration to solution of high concentration, through a semipermeable membrane. When a plant cell is filled with water the guard cells swell up. Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substances—i.e.,.
[noun] movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of higher solute concentration that tends to equalize the. This is a passive process. As no energy is needed.
Osmosis of water from an area of lower to an area of higher solute concentration across a semipermeable membrane. Water readily crosses a membrane down its potential gradient from high to low. The process of osmosis is the dispersal of solvent molecules across a semipermeable membrane,.









