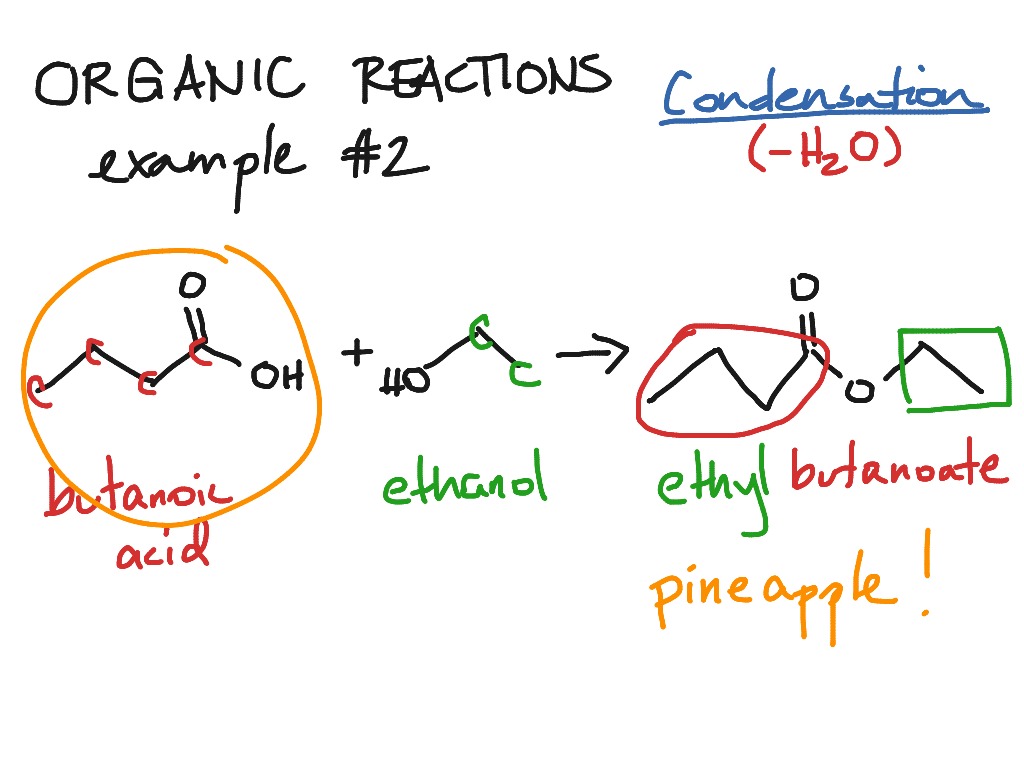
In organic chemistry a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule usually with the loss of a small molecule.
What does condensation mean in chemistry. After 10 minutes, remove the plastic cup from the freezer and place on a. This is a reaction in which two molecules come together to form one single molecule. In general, condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gas phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporisation.
A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction between two compounds where one of the products is water, ethanol, acetic acid, hydrogen sulfide, or ammonia. Usually, a small molecule, which is mostly water, is removed during. Condensation in organic chemistry condensation is also used to describe many varieties of organic reactions.
Condensation can be achieved in one of the following two ways. Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization.the word most often refers to the water cycle. Condensation has multiple meanings in the field of biology.
Fill a clear plastic cup about halfway with water and place in the freezer. It can occur on a small scale, such as water vapour in the air condensing into water droplets on. If a condensation reaction happens between.
It can occur on a small scale, such as water vapour in the air condensing into water droplets on. A condensation reaction is when two smaller molecules join to form a larger one by removing functional groups. Condensation is the resultant substance of a phase change of that substance, from a vapor phase to a liquid phase
Inorganic chemistry is defined as a reaction between two or more. Condensation is a natural process that occurs because of a change in temperature. Condensation is a natural process that occurs because of a change in temperature.









