Bound morphemes can do one of two different jobs.
What are inflectional morphemes. The list of inflectional morphemes includes: Inflectional morphemes are suffixes that get added to a word, thus, adding a grammatical value to it. Inflectional morphemes and meanings [w]hereas a derivational morpheme relates more to the identity of a word itself (in that it more directly affects the meaning of the stem), an inflectional.
Introduction in terms of both form and meaning, inflectional morphology occupies an unusual position in language, as. When a word is inflected, it still retains its core meaning, and its category stays the same. Inflectional morphemes are morphemes that add grammatical information to a word.
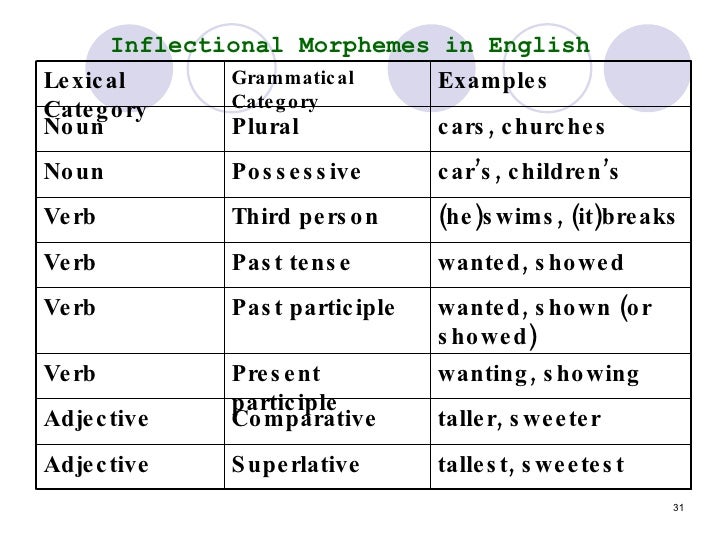
The morphemes of an inflectional morpheme do not create a new word, but they change what a word does in terms of grammar. In the modern english language, only eight inflectional morphemes are used and all of. Inflectional morphemes modify the tense, aspect, mood, person, or number of a verb, or the number, gender, or case of a noun, adjective, or pronoun, without affecting the.
Derivational morphemes often change the part of speech of a word. Inflectional morphemes are bound morphemes that only occur as part of a word and change the grammar of the word, not the meaning. They tend to represent an inflected word’s morphosyntactic content as a.
Thus, there are only 8 inflectional morphemes that indicate at the form and the tense of a word. For example, tall and taller are both adjectives. Inflectional morphology conveys grammatical information, such as number, tense, agreement.
First, inflectional morphemes never change the grammatical category (part of speech) of a word. It can assign a tense, a number, a comparison, or a possession. Inflectional morphemes change what a word does in terms of grammar, but does not create a new word.








/Meaning-and-Examples-of-Inflectional-Morphemes-1691064-v1-dbae2dc94e114a07980162bc82dd014f.png)
