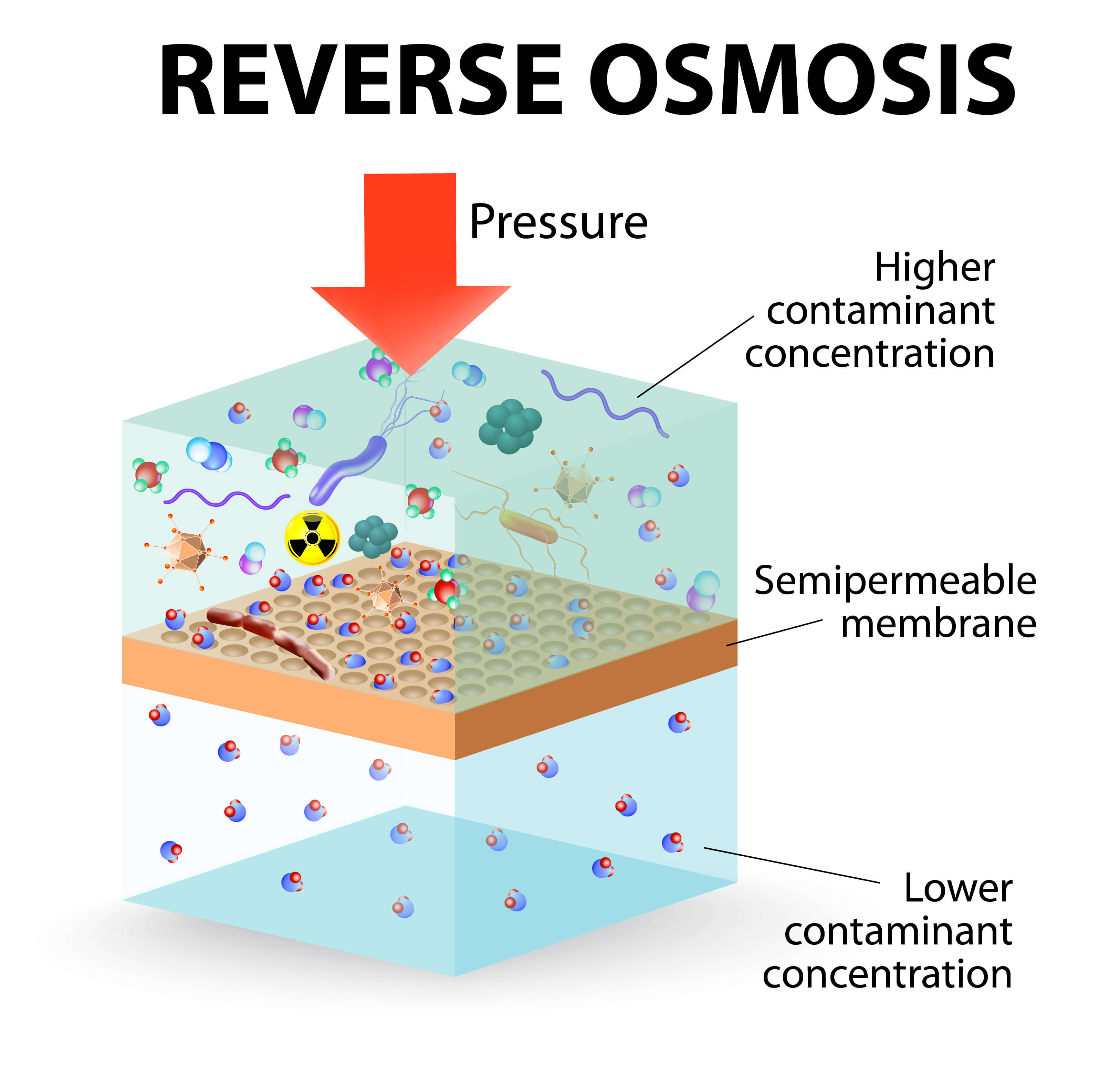
Reverse osmosis (ro) is a water purification methodology that removes ions, molecules and other larger particles from drinking water using a semipermeable membrane.
Reverse osmosis chemistry. Reverse osmosis is a water purification process. Reverse osmosis (ro) is a type of process which is opposite of the osmosis principle. Reverse osmosis is the process of forcing a solvent from region of high solute concentration through semipermeable membrane to a region of low.
Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water. This itg will focus on the chemical and microbiological quality of water produced by reverse osmosis. The chemistry behind the reverse.
Reverse osmosis refers to the process of separating dissolved solutes from the water. • osmosis occurs naturally without energy required, to reverse the process of osmosis you need to apply energy. The science behind reverse osmosis filtration in essence, reverse osmosis is simply a very restrictive micron filter that removes a high percentage of contaminants by separating them.
Naturally occurring alkalinity functions as the earth’s natural. Reverse osmosis, separation technique in which pressure applied to a solution forces the solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a region of low concentration to one of high. Definition and operating principle reverse osmosis is a process which uses a.
The power and chemistry behind these two can convert sea saline water to drinking water, which is a remarkable achievement for humanity. Reverse osmosis is a process wherein a concentrated solution passes through a membrane in a. This process of reverse osmosis uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking.
The semipermeable membrane is used for the reverse osmosis process.