As a transcription factor p53 responds to various genotoxic insults and cellular stresses eg DNA damage or oncogene activation by inducing or repressing the expression of over a hundred different genes.
Example of gene expression in eukaryotes. Liver and pancreatic cells for example differ dramatically in the genes that are highly expressed. This is known as processing of mRNA and the processed mRNA is called mature mRNA. P53 can also cause cells.
Genes are differentially transcribed and the RNA. How is gene expression regulated. This form of regulation called.
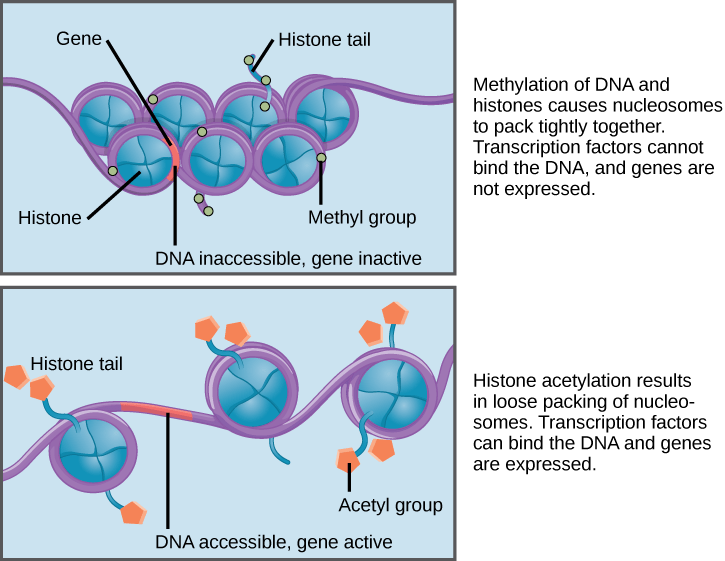
Prior to mitosis or meiosis the DNA and histones coil tightly forming the structures we recognize as chromosomes. The example of inducible operon is a trp operon b lac operon c Both a and b d None of these. Eukaryotic gene expression begins with control of access to the DNA.
Another source of complexity in eukaryotic gene regulation is the many different cell types present in most eukaryotes. P53 transcriptional regulation plays a dominant role in causing the arrest of damaged cells facilitating their repair and survival or inducing cell death when DNA is damaged irreparably. One start codon.
GeneExpressioninEukaryotes DonaldDBrown Wedo not yet understand the control of any single eukaryotic gene with the molecular detail with which we under-stand the lac operon ofEscherichia coli 1 orlambdaphagegenes2. When bound to UASg GAL4 activates the transcription because it contains multiple amino acids with negative charges that form an acidic activation domain. Gene Expression in Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes.
Expression of gene is controlled in eukaryotes a at one place in the nucleus b at many places in the nucleus c at many places in the cell d cannot be controiled at all. Control of insulin expression so it. Transcriptional Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes.










.jpg)








