Watch the bonus round to see multiple examples of dead weight loss.
Deadweight loss on graph. Then, the new price (p2) and quantity (q2) have to be found. When the tax is imposed, the price paid by buyers increases, and the price received by seller decreases. When a tax is levied on buyers, the demand curve shifts downward in accordance with the size of the tax.
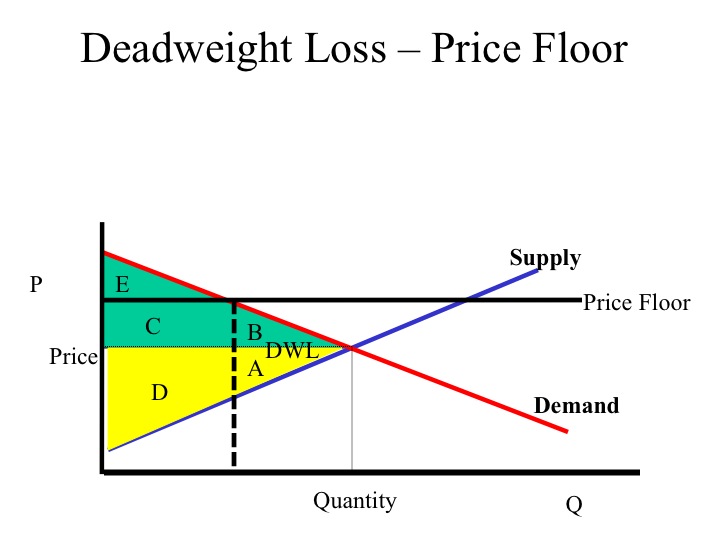
A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market. The deadweight loss calculator helps you understand and calculate the economic cost to society when cournot dead weight loss on graph factors impact market prices. In the deadweight loss graph below, the deadweight loss is represented by the area of the blue triangle, which is equal to the price difference (base of the triangle) multiplied by the quantity.
First, you need to determine the price (p1) and quantity (q1) using supply and demand curves as shown in the graph; The producer surplus can be found by. Deadweight loss graph using the minimum wage example;
Example breaking down tax incidence. Deadweight loss is used to calculate the value of the deadweight loss at various stages,. My explanation of deadweight loss (aka.
Therefore, buyers and sellers share the burden of the tax, regardless of how it is imposed. Please keep in mind that these. Notice that monopolies charge a higher price and produce.
It can visually be portrayed what effects it has on consumer and producer surpluses and how that relates to. In the graph, the equilibrium point is denoted by f and the quantity by ob. We know the appropriate demand and supply functions, and we know that without the subsidy, we.









