Firstly, plot graph for the supply curve and the initial demand curve.
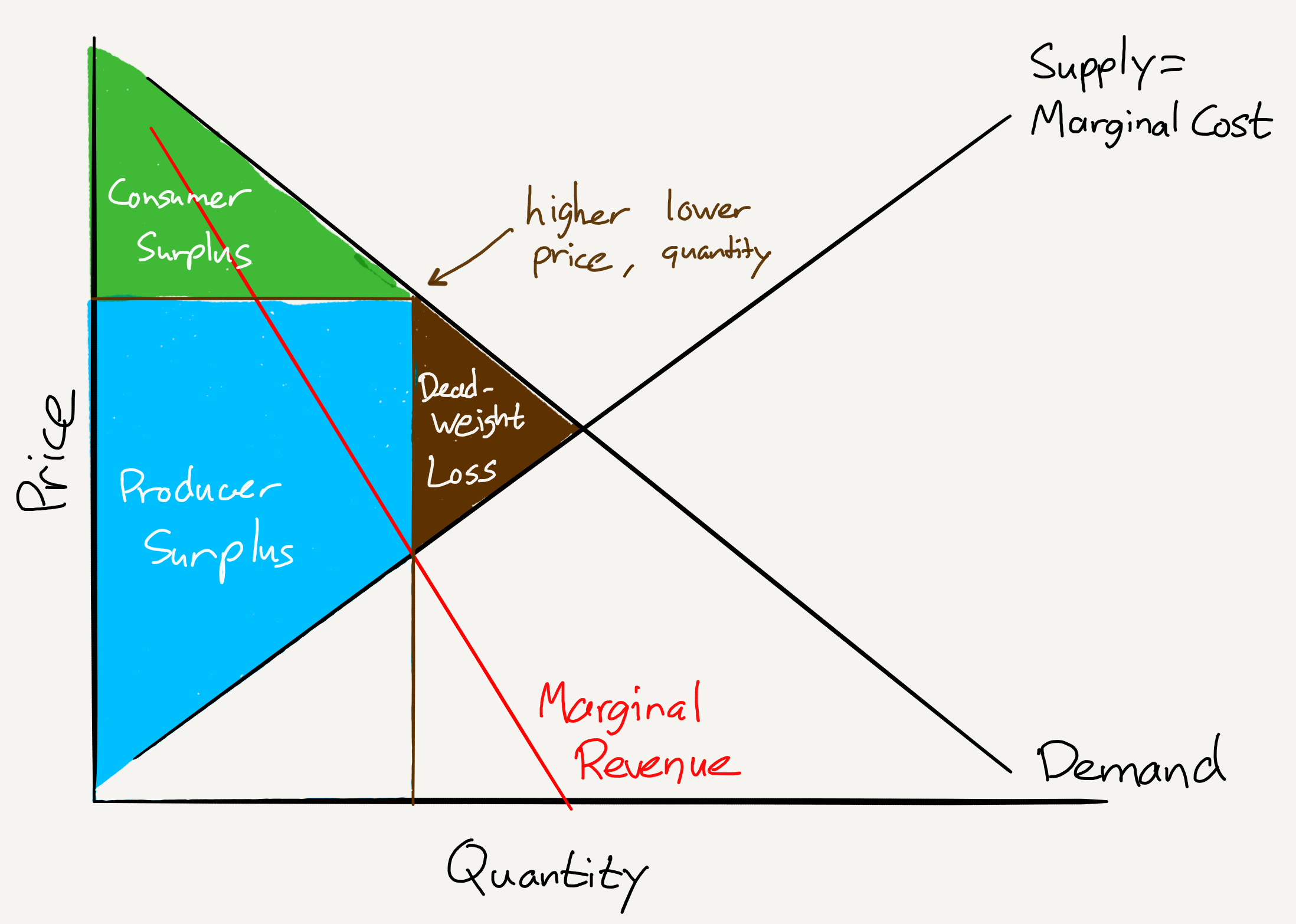
Deadweight loss in monopoly graph. This will be at output qm and price pm. A deadweight loss happens when a company is able to charge a higher price for its product or service, and as a result, some of its customers are priced out of purchasing the product or. The distinction between the two lies in the fact that taxes are public and administered.
A deadweight loss occurs with monopolies in the same way that a tax causes deadweight loss. The unit of the deadweight loss is the dollar amount of the reduction in total economic surplus. A monopoly makes a profit equal to total revenue minus total cost.
That is the most competitive of markets. Determine the original quantity and new quantity. Finally, click on cells b18, b19, and b21 to show the consumers’ surplus ( cs ), producers’ surplus ( ps ), and deadweight loss ( dwl) from the monopoly solution in the chart.
Deadweight loss occurs when an economys welfare is not at the. When the total output is less than socially optimal, there is a deadweight loss, which is indicated by the red area in figure. A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where mr = mc.
Why does a monopoly cause a deadweight loss quizlet? Updated 8/3/2020 jacob reed in the last review, we covered the perfectly competitive market structure. Keys to understanding the monopoly graph.
Calculating deadweight loss can be summarized into the following three steps: The formula to make the calculation is: How does a monopoly cause deadweight loss?.








