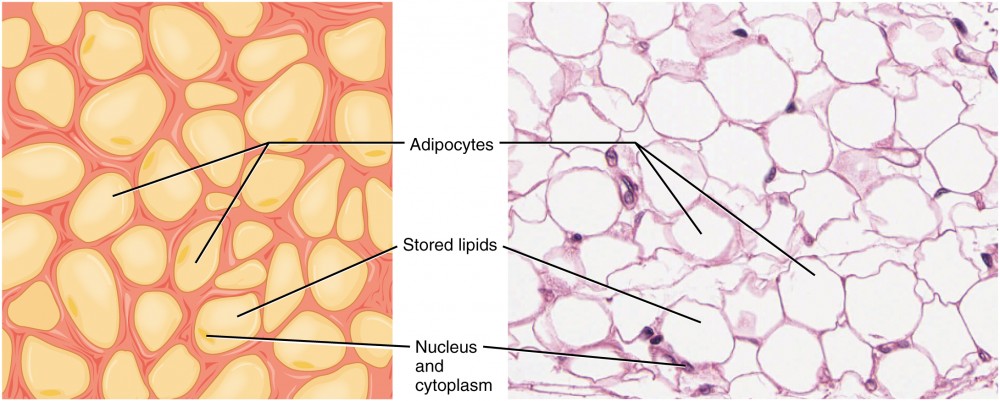
Hello, in this particular article you will provide several interesting pictures of yellow fat function.html. We found many exciting and extraordinary yellow fat function.html pictures that can be tips, input and information intended for you. In addition to be able to the yellow fat function.html main picture, we also collect some other related images. Find typically the latest and best yellow fat function.html images here that many of us get selected from plenty of other images.
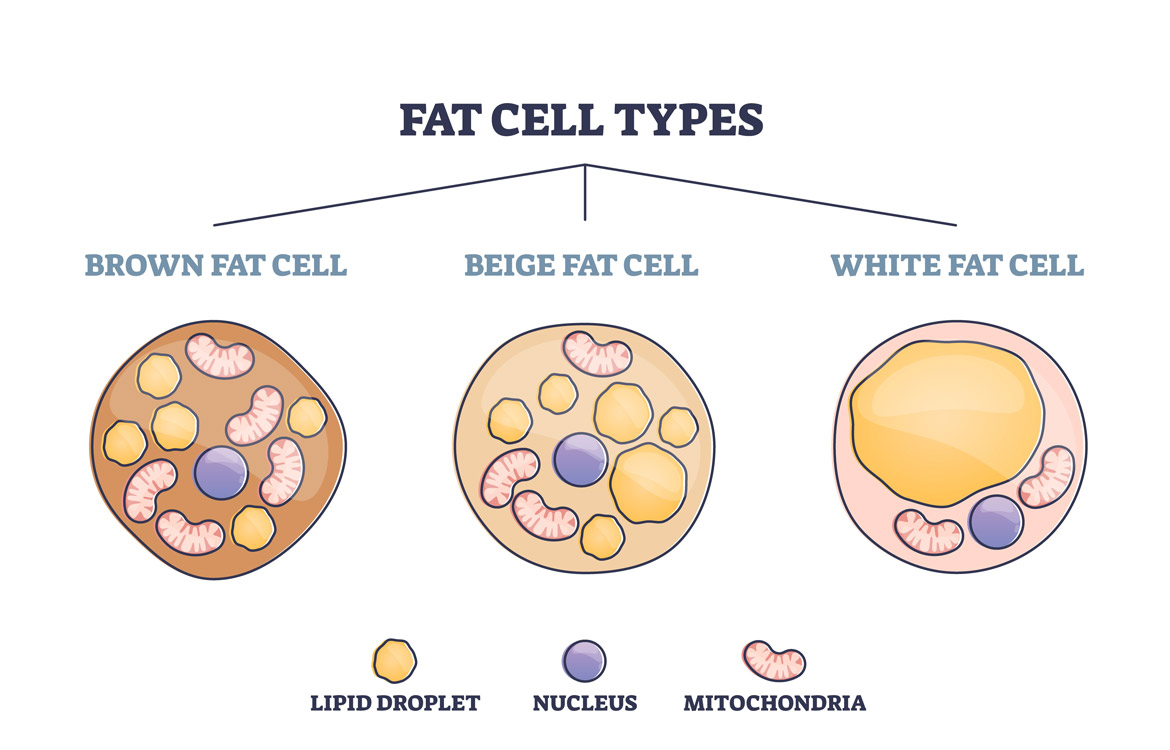 We all hope you can get actually looking for concerning yellow fat function.html here. There is usually a large selection involving interesting image ideas that will can provide information in order to you. You can get the pictures here regarding free and save these people to be used because reference material or employed as collection images with regard to personal use. Our imaginative team provides large dimensions images with high image resolution or HD.
We all hope you can get actually looking for concerning yellow fat function.html here. There is usually a large selection involving interesting image ideas that will can provide information in order to you. You can get the pictures here regarding free and save these people to be used because reference material or employed as collection images with regard to personal use. Our imaginative team provides large dimensions images with high image resolution or HD.
 yellow fat function.html - To discover the image more plainly in this article, you are able to click on the preferred image to look at the photo in its original sizing or in full. A person can also see the yellow fat function.html image gallery that we all get prepared to locate the image you are interested in.
yellow fat function.html - To discover the image more plainly in this article, you are able to click on the preferred image to look at the photo in its original sizing or in full. A person can also see the yellow fat function.html image gallery that we all get prepared to locate the image you are interested in.
 We all provide many pictures associated with yellow fat function.html because our site is targeted on articles or articles relevant to yellow fat function.html. Please check out our latest article upon the side if a person don't get the yellow fat function.html picture you are looking regarding. There are various keywords related in order to and relevant to yellow fat function.html below that you can surf our main page or even homepage.
We all provide many pictures associated with yellow fat function.html because our site is targeted on articles or articles relevant to yellow fat function.html. Please check out our latest article upon the side if a person don't get the yellow fat function.html picture you are looking regarding. There are various keywords related in order to and relevant to yellow fat function.html below that you can surf our main page or even homepage.
 Hopefully you discover the image you happen to be looking for and all of us hope you want the yellow fat function.html images which can be here, therefore that maybe they may be a great inspiration or ideas throughout the future.
Hopefully you discover the image you happen to be looking for and all of us hope you want the yellow fat function.html images which can be here, therefore that maybe they may be a great inspiration or ideas throughout the future.
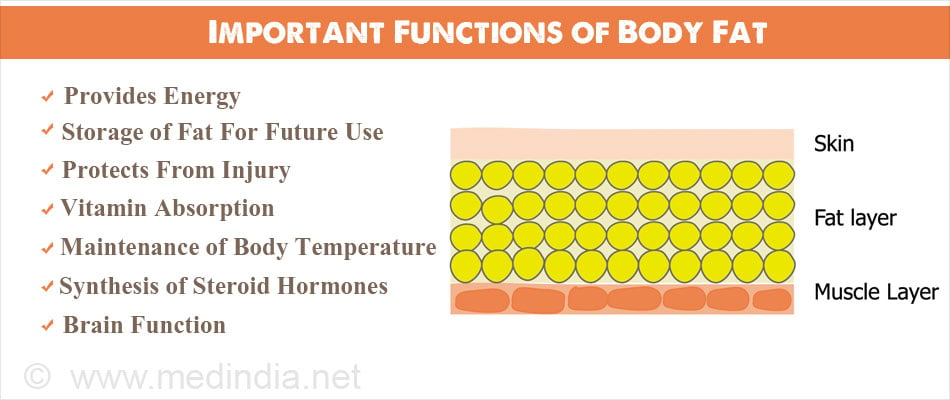 All yellow fat function.html images that we provide in this article are usually sourced from the net, so if you get images with copyright concerns, please send your record on the contact webpage. Likewise with problematic or perhaps damaged image links or perhaps images that don't seem, then you could report this also. We certainly have provided a type for you to fill in.
All yellow fat function.html images that we provide in this article are usually sourced from the net, so if you get images with copyright concerns, please send your record on the contact webpage. Likewise with problematic or perhaps damaged image links or perhaps images that don't seem, then you could report this also. We certainly have provided a type for you to fill in.
 The pictures related to be able to yellow fat function.html in the following paragraphs, hopefully they will can be useful and will increase your knowledge. Appreciate you for making the effort to be able to visit our website and even read our articles. Cya ~.
The pictures related to be able to yellow fat function.html in the following paragraphs, hopefully they will can be useful and will increase your knowledge. Appreciate you for making the effort to be able to visit our website and even read our articles. Cya ~.
 Function of Fats
Function of Fats
 Fit 4 Lyfe™ on Twitter: "Carbs, Fats, & Protein are the three macro
Fit 4 Lyfe™ on Twitter: "Carbs, Fats, & Protein are the three macro

 PPT - Lipids: Fats and Oils PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID
PPT - Lipids: Fats and Oils PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID
 CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF FATS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS | PPT
CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF FATS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS | PPT
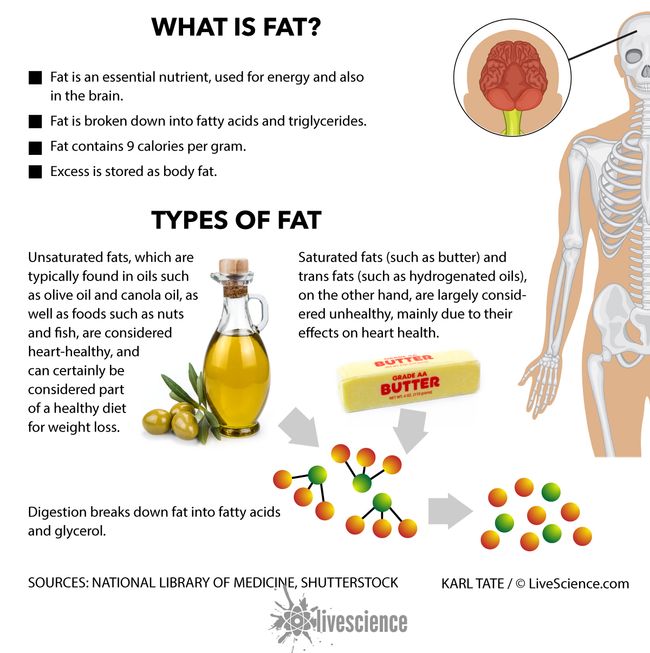 What Are Triglycerides? | Live Science
What Are Triglycerides? | Live Science
 PPT - Basic Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:5627683
PPT - Basic Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:5627683
 PPT - All about Fats PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2378251
PPT - All about Fats PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2378251
 PPT - Basic Human Needs Nutrition PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT - Basic Human Needs Nutrition PowerPoint Presentation, free
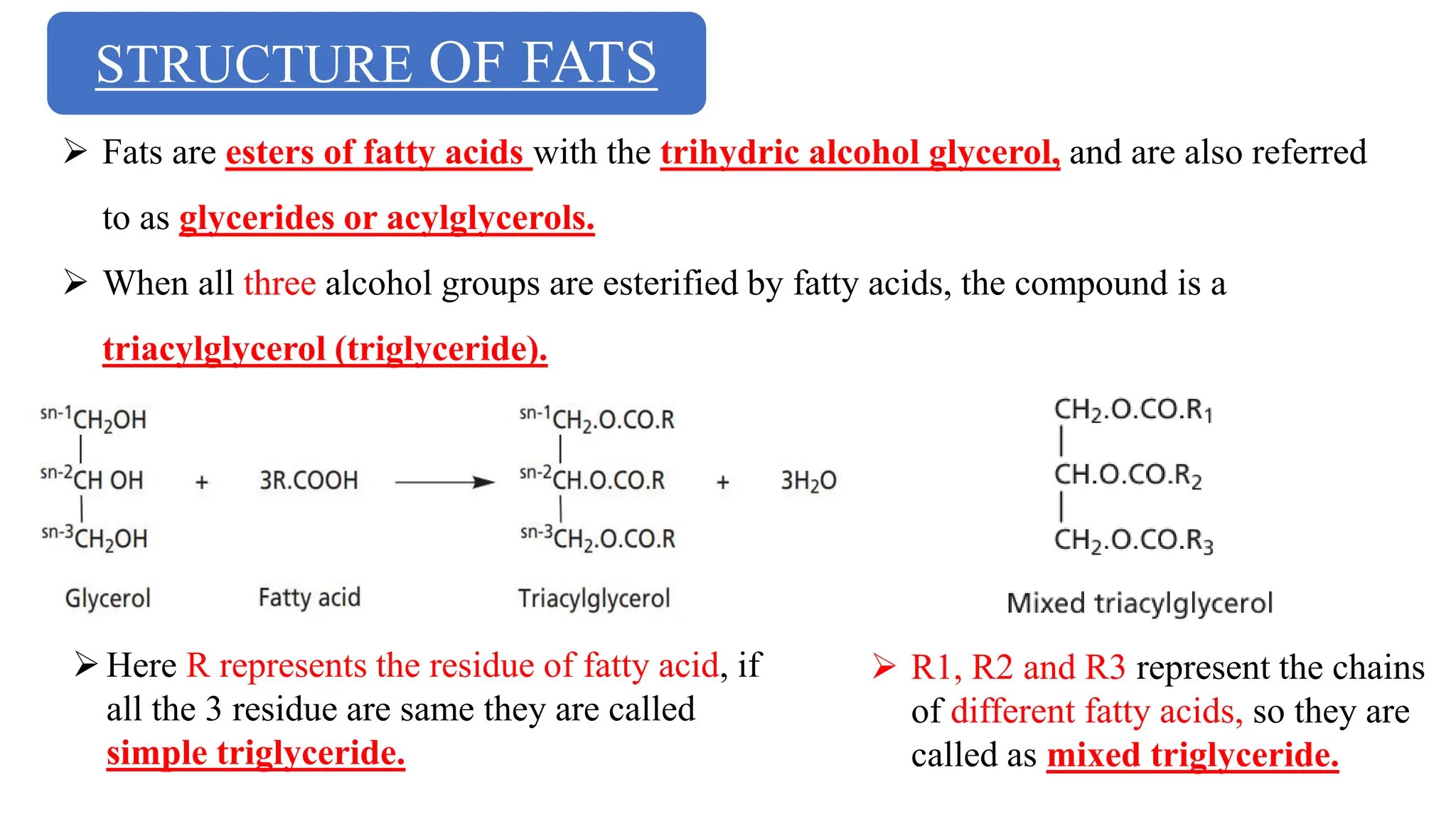 CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF FATS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS | PPT
CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF FATS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS | PPT
 Functions of Fats|For CSS and PMS Aspirants|Food science | - YouTube
Functions of Fats|For CSS and PMS Aspirants|Food science | - YouTube
 PPT - Fats PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:4139464
PPT - Fats PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:4139464

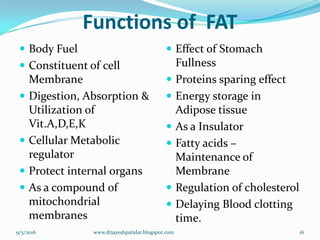 Fats as a nutrient | PPT
Fats as a nutrient | PPT