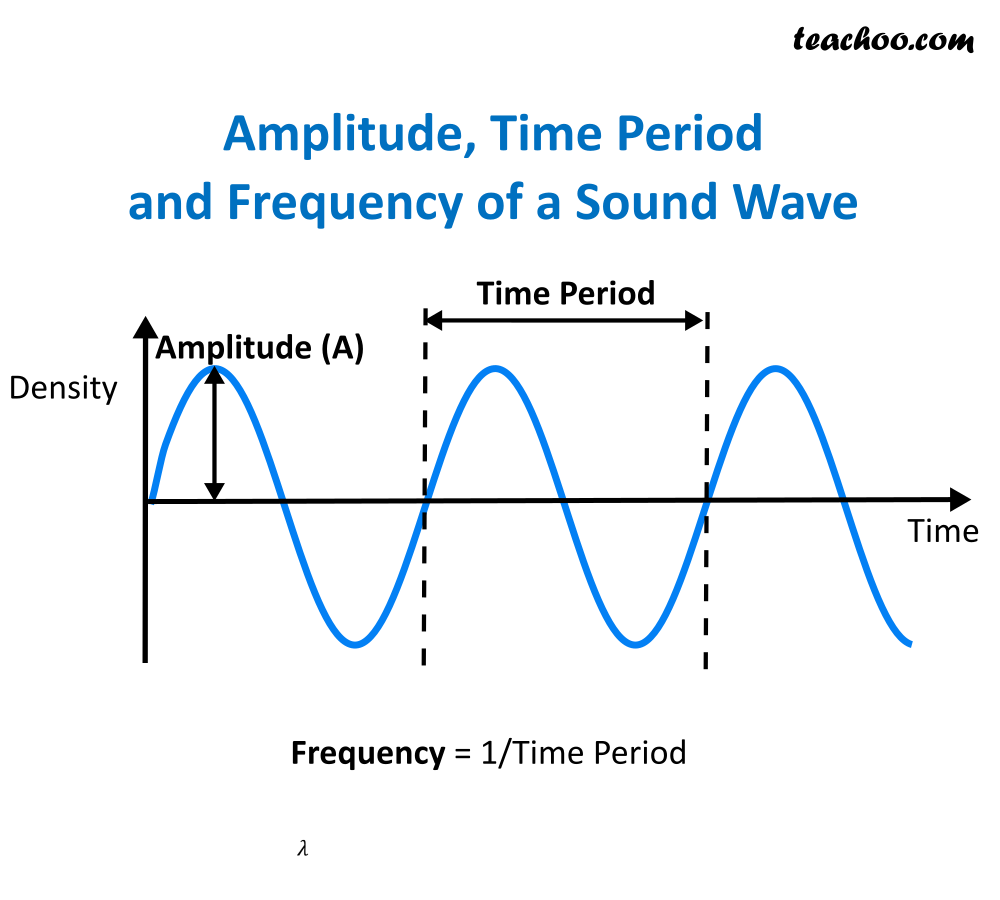
Wavelength can be defined as the distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave.
What is wavelength in science. Wavelength, distance between corresponding points of two consecutive waves. Wavelength is the distance between two crests or two troughs as shown in fig. Wavelength is related to the speed at which sound travels and can be calculated by dividing the speed of.
Forms of electromagnetic radiation like radio waves, light waves or infrared (heat) waves make characteristic patterns as they travel through space. Alternately, we can measure from the. Thinking back to our ocean example, to measure the wavelength we would measure the.
A particular course or line of thought especially as related. It is measured in the direction of the wave. Wavelength modulation, which has been employed with continuum source and laser.
The distance in the line of advance of a wave from any one point to the next point of corresponding phase 2 : The distance between one peak or crest of a wave of light, heat, or other energy and the next peak or crest sentences: The relationship between energy (e), frequency and wavelength can be described with this equation:
It is expressed in nm in the “electronic spectrum.” 1 nm = 10 −9 m. The wavelength of a wave describes how long the wave is. The distance from the crest (top) of one wave to the crest of the next wave is the wavelength.
The wavelength (or alternatively wavenumber or wave vector) is a characterization of the wave in space, that is functionally related to its frequency, as constrained by the physics of the system. Nasa's satellites study different wavelengths of light from. Wavelength can be defined as the distance between the two consecutive crests or troughs in a curve.








