What is osmosis and reverse osmosis in chemistry?
What is reverse osmosis in chemistry. Reverse osmosis is a water purification process. When two aqueous solutions of different. It is the best method for water softening.
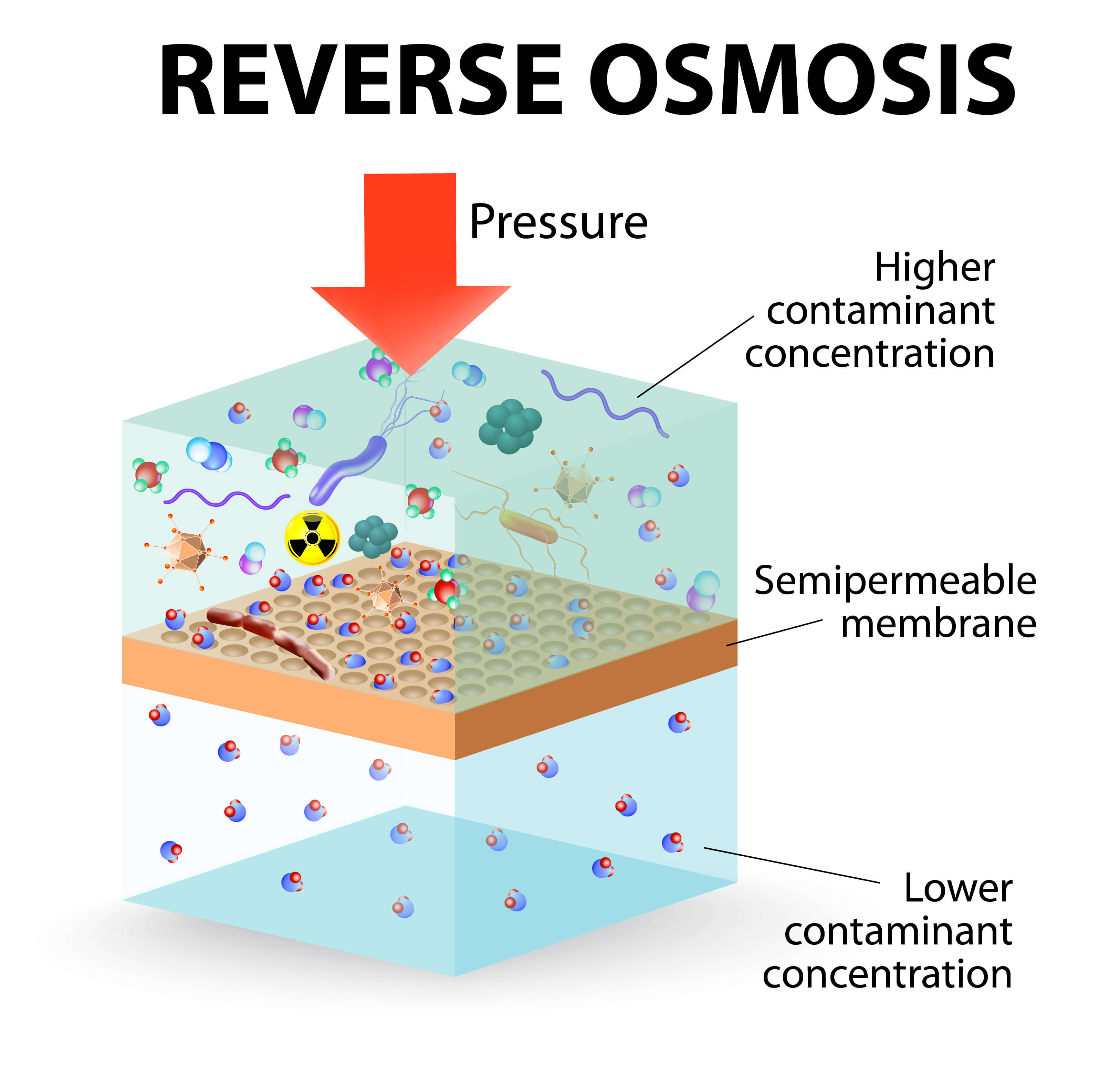
The semipermeable membrane will block all. Reverse osmosis chemistry — basics, barriers and breakthroughs 1. Osmosis is a process in which liquid water flows through a semipermeable membrane from a diluted solution into a more concentrated.
This is done by creating a pressure gradient between. Reverse osmosis is a process that uses pressure to force water through a membrane in order to purify it of dissolved salts and other contaminants. Press question mark to learn the rest of the keyboard shortcuts.
Reverse osmosis (ro) is a standard method of filtration typically used for the removal of molecules and ions present in a solution. Press j to jump to the feed. Reverse osmosis (ro) is a water purification methodology that removes ions, molecules and other larger particles from drinking water using a semipermeable membrane.
A community for chemists and those who love chemistry. Reverse osmosis (ro) is defined by mindler and epstein (1986) as ‘a pressure driven separation of water from a saline solution across a membrane, the pressure being. Some of the advantages of the reverse osmosis process are as follows.
There is an inherent difference in the separation mechanism in all filtration processes and the reverse. This process of reverse osmosis uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking. The rapidly increasing introduction of reverse osmosis (ro) membrane plants around the world.