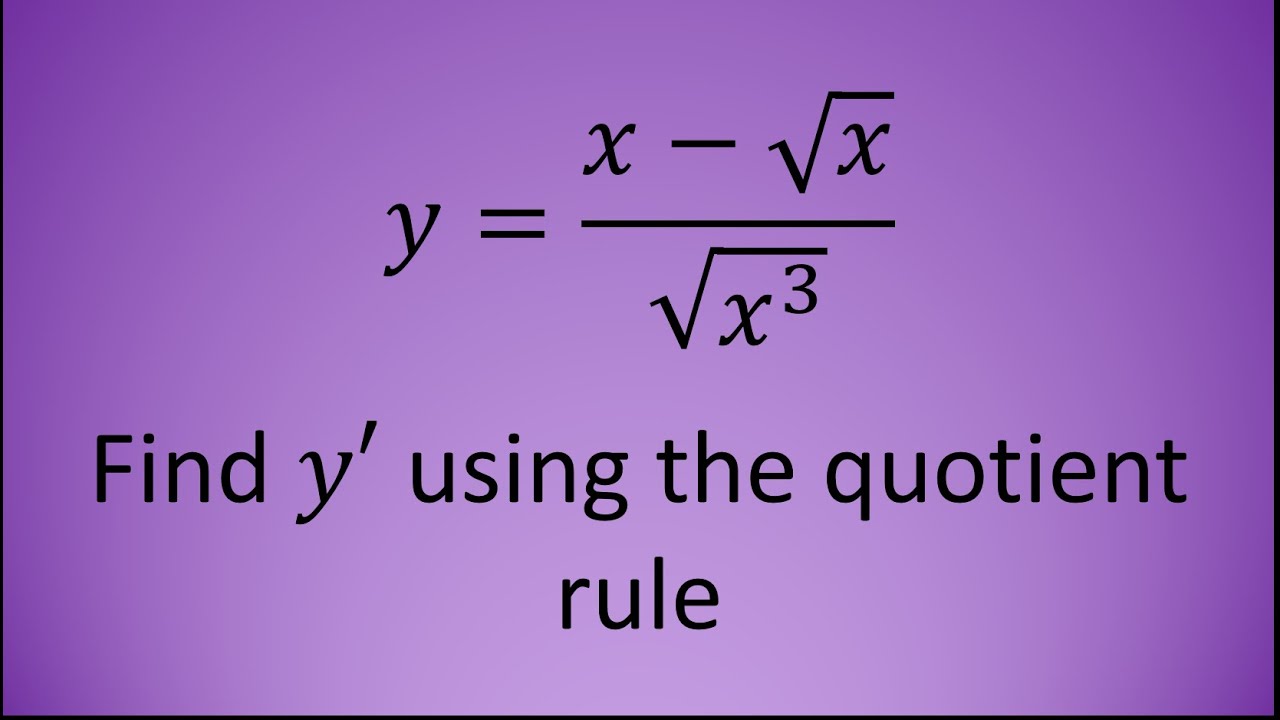
If you have been stuck in the middle of calculating any complex math problems because of finding the quotient for large numbers?
What is quotient. The degree to which a specific quality or. A quotient is the result of a division problem. The quotient is defined as the quantity produced after dividing.
A quotient can be an integer in the case of euclidean division, a fraction, or a ratio in the case of a proper division. Quotiens 'how many times', pronounced / ˈ k w oʊ ʃ ən t /) is a quantity produced by the division of two numbers. In calculus, the quotient rule is a method for determining the derivative (differentiation) of a function in the form of the ratio of two differentiable functions.
Britannica dictionary definition of quotient. The number of times one quantity is contained in another. [noun] the number resulting from the division of one number by another.
Given two differentiable functions, f(x) and g(x), where f'(x) and g'(x) are their. Find the difference quotient for the following function: When you compute the quotient in division, you may end up with a remainder.
The result of division is called the quotient. The quotient rule is a formula that is used to find the derivative of the quotient of two functions. In this step, i’m replacing the “f (x+h)” in the left hand.
The answer after we divide one number by another. It’s also utilized in the derivative definition. Iq, which stands for intelligence quotient, is a score that is derived from a collection of tests designed to determine how mentally agile or intelligent a person is.









