Osmosis is a critical process in biological organisms, helping control levels of molecules like lipids, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water, and oxygen.
What is osmosis definition. Movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of higher solute concentration that tends to equalize the concentrations of solute. The tendency of a fluid, usu. The process that causes a liquid (especially water) to pass through the wall of a living cell.
Water, to pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution where the solvent concentration is higher, thus. Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substances—i.e.,. We'll focus on osmosis in biology in a bit;
Britannica dictionary definition of osmosis. An ability to learn and. In biology, osmosis refers to the net movement of water molecules through cell membranes.
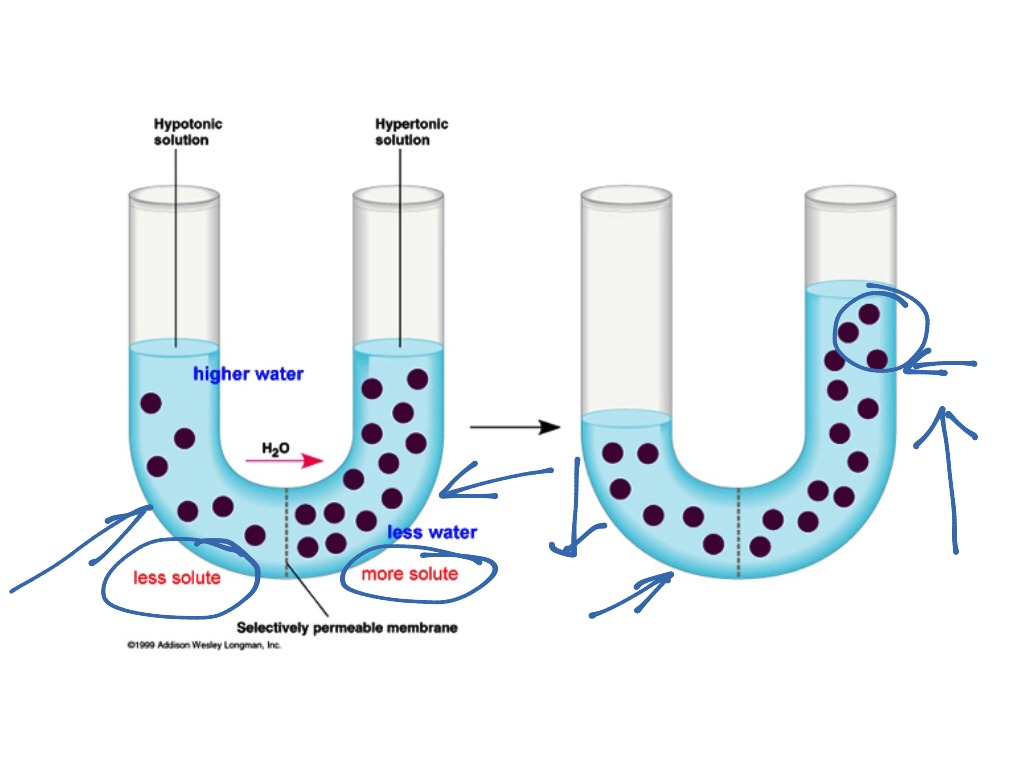
This is a passive process. For now, let's continue with our general overview of. Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules from solution of low concentration to solution of high concentration, through a semipermeable membrane.
The process by which solvent molecules pass from a solution of lower concentration to a solution of higher concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Two types of osmosis are. Osmosis and osmotic pressure is a thermodynamic concept which exists independently of mechanism.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules, from a region where the water molecules are in higher concentration, to a region where they are in lower concentration, through a partially.









