
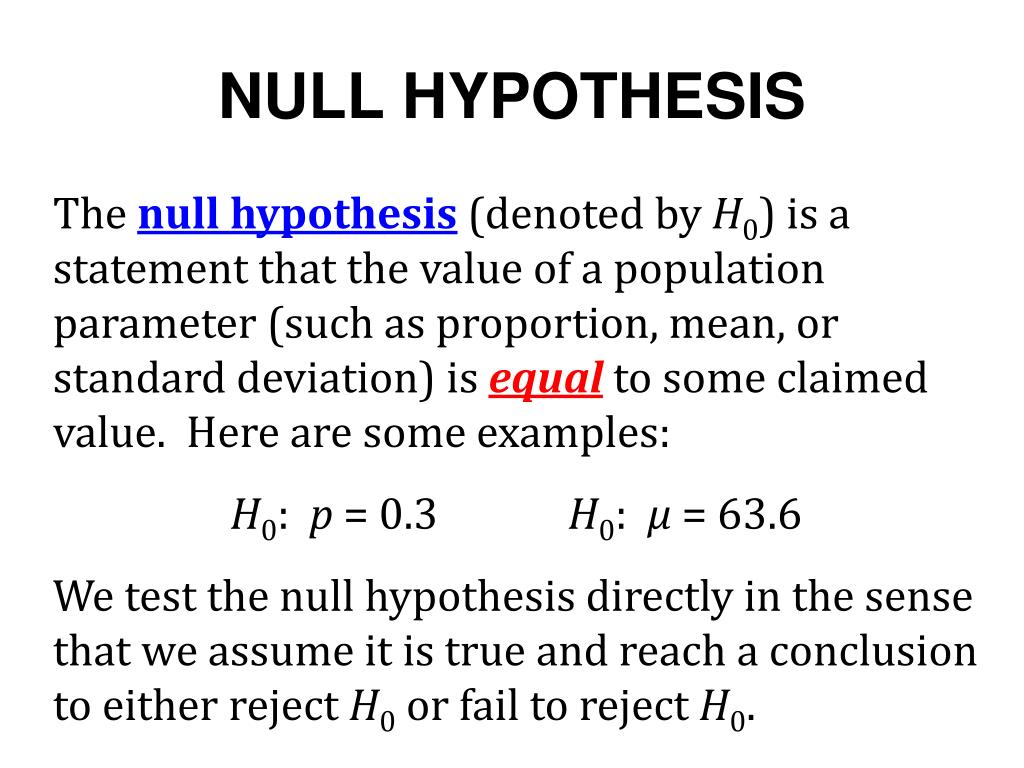
Population parameter =, ≤, ≥ some value.
What is null hypothesis in statistics. The null hypothesis is a statement of equality and acts as a starting point accepted as true in the absence of additional information. The null hypothesis states that the population parameter equals a particular value. Its usefulness is sometimes challenged, particularly.
Typically, the null hypothesis includes an equal sign. That value is usually one that represents. The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
The word ‘null’ can be thought of as ‘no change’. What is a null hypothesis? A null hypothesis is a hypothesis that says there is no statistical significance between the two variables in the hypothesis.
Note that the null hypothesis always. Population parameter <, >, ≠ some value. In a mathematical formulation of the null hypothesis, there will typically be an equal sign.
This null hypothesis can be written as: States that two factors or groups are unrelated and there is no difference between certain characteristics of a population. The null hypothesis states there is no relationship between the measured phenomenon (the dependent variable) and the independent variable.
For most of this textbook, the null hypothesis is that the means of the two groups are similar. E.g., a null hypothesis may state that the population mean return is equal to zero. The null hypothesis is a typical statistical theory which suggests that no statistical relationship and significance exists in a set of given single observed variable, between two sets of observed.








/null-hypothesis-vs-alternative-hypothesis-3126413-v31-5b69a6a246e0fb0025549966.png)