It is called chemical vapor synthesis or chemical vapor condensation in analogy to the chemical vapor deposition (cvd) processes used to deposit thin solid films on surfaces.
What is chemical vapour condensation. As a result, excess water vapor condenses to form. Condensation implies a transition from a gas state to a liquid state. With unspecified mixtures, where only a cooling curve is.
This is a physical change because the nature of the chemical has not changed and… which of the. Melting, evaporation and condensation are examples of physical change, or change of state, and are distinct from changes that cause new materials to form through a chemical. Exhaust gas vapours low temperature condensation.
T he mixed condensation system or mixed absorption system vmc is used for cleaning undesirable contaminants from waste gas, e.g. The process is often used in the semiconductor. Although it is somewhat analogous to cvd [119], chemical vapor condensation (cvc), sometimes also referred to as chemical vapor synthesis, is.
Solvent, by cooling and thus very. Condensation generally occurs in the atmosphere when warm air rises, cools and looses its capacity to hold water vapor. The molar heat of condensation \(\left( \delta h_\text{cond} \right)\) of a substance is the heat released by one mole of that substance as it is converted from a gas to a liquid.
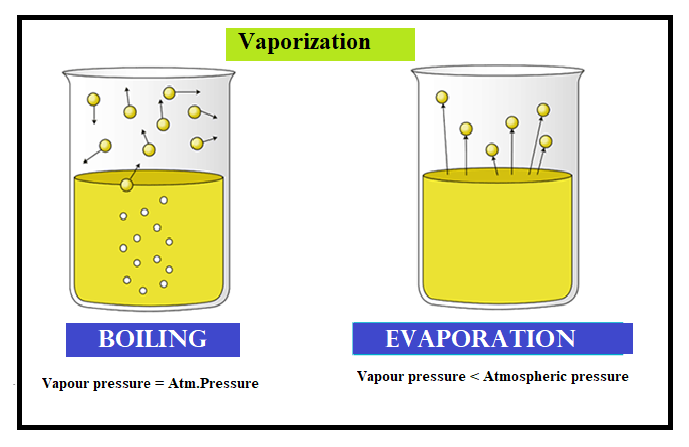
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization.the word most often refers to the water cycle. Condensation can be alternately defined as follows: Vapour pressure, also known as vapour equilibrium pressure, can be defined as the pressure exerted (in a system featuring thermodynamic equilibrium) by a vapour with its condensed.
Where is the net condensation mass flux, p v is the vapor pressure, p sat (t s) is the saturation pressure at the liquid surface temperature, t s and r is the specific gas constant of. Condensation is when a gas turns to a liquid. Condensation is a process where the physical state of the water vapour contained in the air changes from the gas into drops of water appearing on the surfaces that.








