Wavelength of a wave and frequency of.
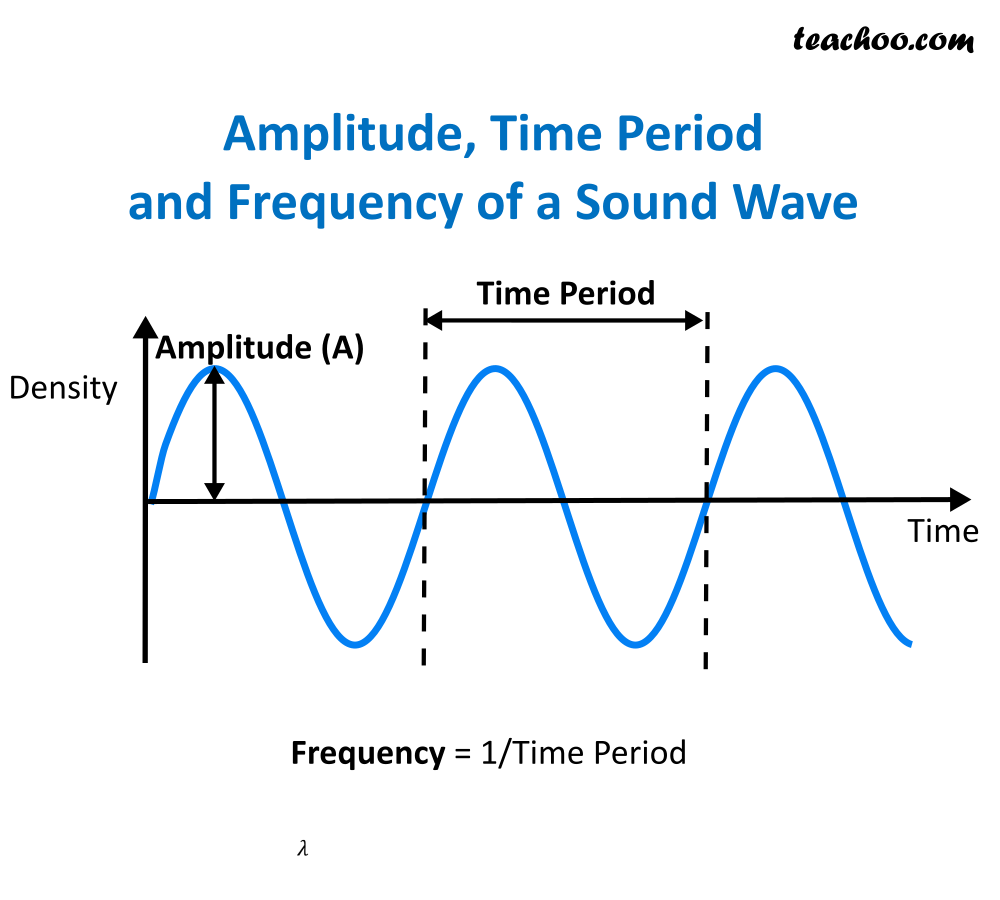
What is a wavelength in science. In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. Wavelength can be defined as the distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave. It is measured in the direction of the wave.
Try adjusting the wavelength below: How is the wavelength of light related to its frequency? The relationship between energy (e), frequency and wavelength can be described with this equation:
Energy of radiation is inversely. Here, we see that f is the wave's frequency, whereas c. The equation we use to donate their motion is the same, which is:
Thinking back to our ocean example, to measure the wavelength we would measure the. For any wave in a medium:. [noun] the distance in the line of advance of a wave from any one point to the next point of corresponding phase.
“corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that have completed identical fractions of their periodic motion. Usually, in transverse waves (waves with points. The distance between one peak or crest of a wave of light, heat,.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. In the same manner, the shorter the. Wavelength = (speed) / (frequency).








