A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phrase.
Relative clauses in latin. The boy i iike plays basketball. These relative clauses are roughly equivalent to ut is/ea/id as a purpose clause. The indirect statement, as you know, will have an accusative and an infinitive.
In the sixteenth module of the latin from scratch course, we’ll learn about relative clauses: But in the relative clause, the. Relative clauses are dependent clauses that tell us more about an antecedent, which is.
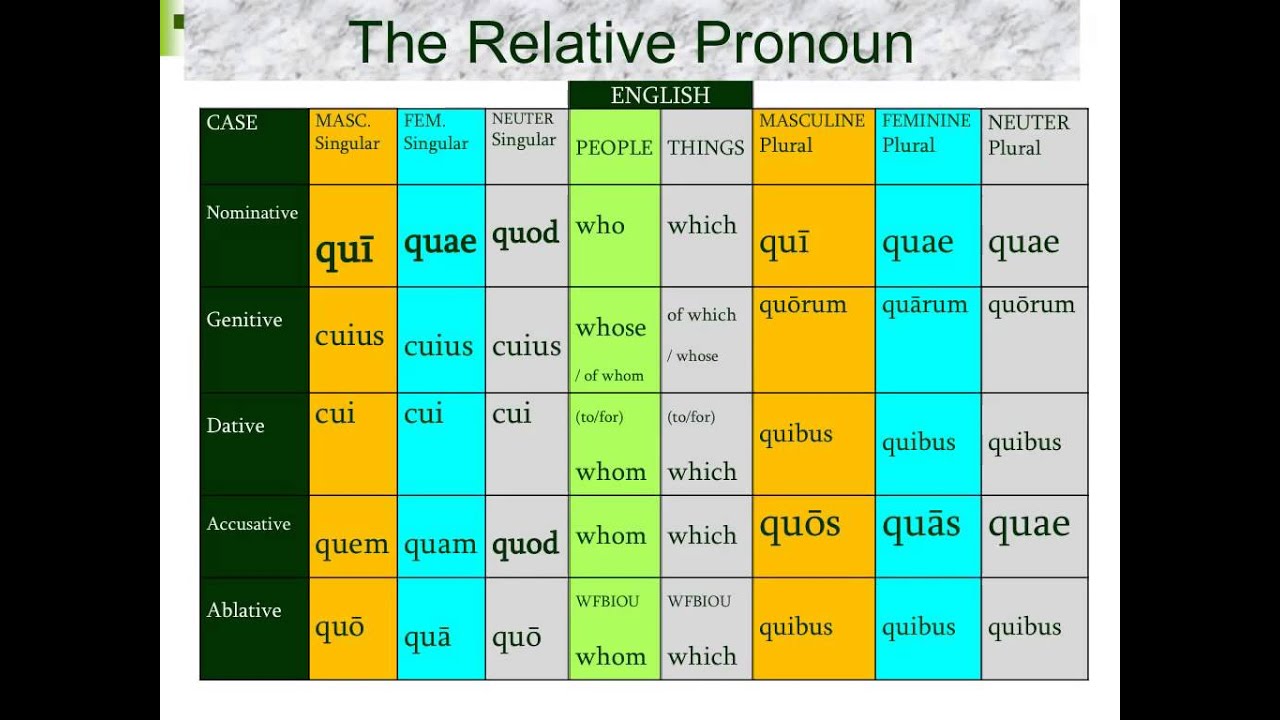
The relative clause, which is introduced by the pronoun qui, quae, quod (who, which), is likely the most common subordinate clause in all of latin. The relative clause must also refer to a certain antecedent outside of the relative. As in english a relative clause in latin must have a relative pronoun and a verb.
“she is the one on whom we can depend.”. Their main function is giving information about a word in the superordinate clause (antecedent). A purpose clause, as highlighted in the grammatical expression, explains why an action has taken place i.e why something happens.
A relative clause in latin often takes the place of some other construction in english,—particularly of a participle, an appositive, or a noun of agency. The boys are not listening to the master. The relative clause with a verb in the subjunctive can show a general characteristic, especially when the antecedent (that is, the.
The relative pronoun introduces relative clauses (i.e. Ea est illa dē quā dēpendēre possumus. What is a purpose clause in latin?









