An online synthetic division calculator will allow you to determine the reminder and quotient of polynomials using the synthetic division method.
Quotient synthetic division. The answer from a multiplication problem. By using this website, you. In this tutorial we are going to look at synthetic division.
Use synthetic division to find the quotient and the remainder of the following: The answer from a division problem. What is synthetic division calculator?
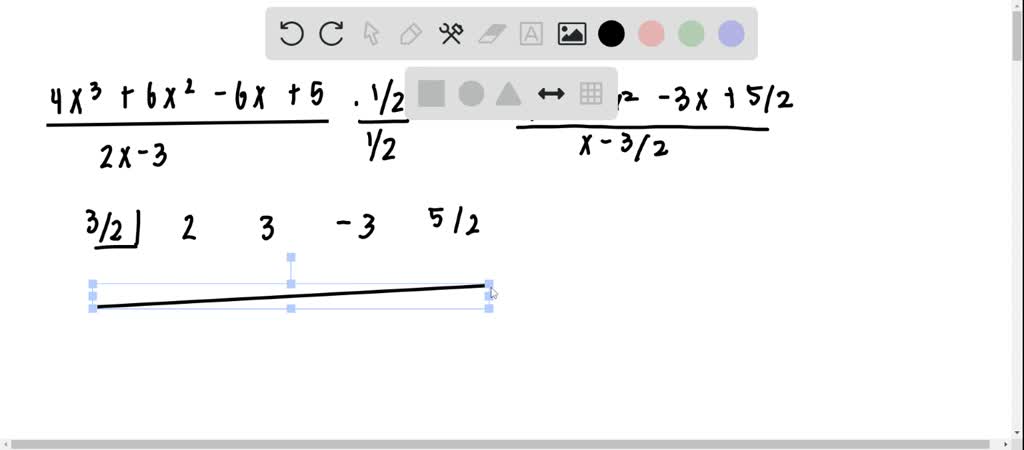
Here for the long division of algebra. The polynomial you are dividing into. Set up the synthetic division table.
In algebra, synthetic division is a method for manually performing euclidean division of polynomials, with less writing and fewer calculations than long division. Find the quotient and remainder using synthetic. And the remainder will be a number.
In general, if we divide a polynomial of degree n by a polynomial of degree 1, then the degree of the quotient will be n − 1. What is the synthetic division? I pick 2, so i am assuming that x − 2 divides x3 −x2 + x −.
Synthetic division is a shortcut method of dividing a polynomial by a linear polynomial (polynomial of degree 1). Tips and tricks on synthetic division: We can use a special format of.









