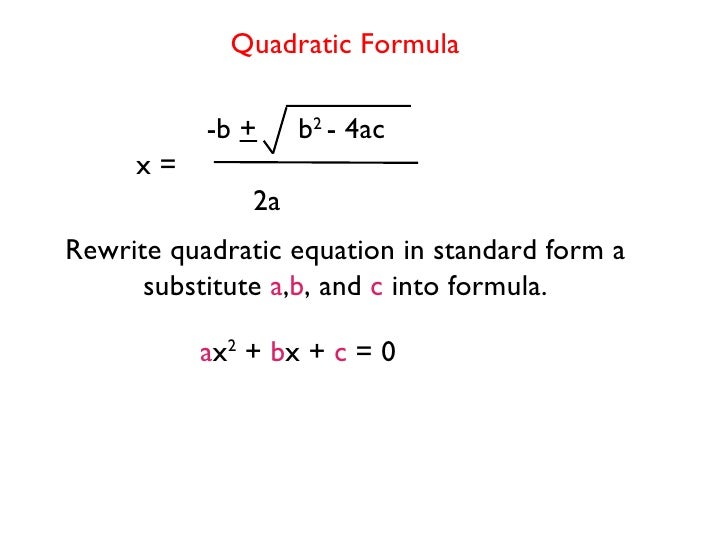
Solve an equation of the form a x 2 + b x + c = 0 by using the quadratic formula:
Quadratic equation in standard form. This is how to write the quadratic function in standard form: And the properties of their graphs such as vertex and x and y intercepts are explored, interactively, using an applet. You can graph a quadratic.
Write the vertex form of a quadratic. A quadratic equation in standard form (a, b, and c can have any value, except that a can't be 0.)here is an example: It has the one unknown value which is x and the a,b,c coefficients which have their own known value.
The quadratic equation in its standard form is ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a and b are the coefficients, x is the variable, and. Since the complex roots always occur in pairs, so the other root is 3 + 2i. Now there's many ways to graph this.
− b ± √ b 2 − 4 a c. Quadratics can be defined as a polynomial equation of a second degree, which implies that it comprises a minimum of one term that is squared. If p (x) is a quadratic polynomial, then p (x) = 0 is called a quadratic equation.
In writing quadratic equation in standard form, we use the format where.examples of quadratic equation in standard form are the following: The standard form of the equation has the form ax^2+bx+c=0. Quadratic functions in standard form.
A quadratic equation is an algebraic equation of the second degree in x. In algebra, a quadratic equation (from latin quadratus ' square ') is any equation that can be rearranged in standard form as. Practice with forms of quadratics.









