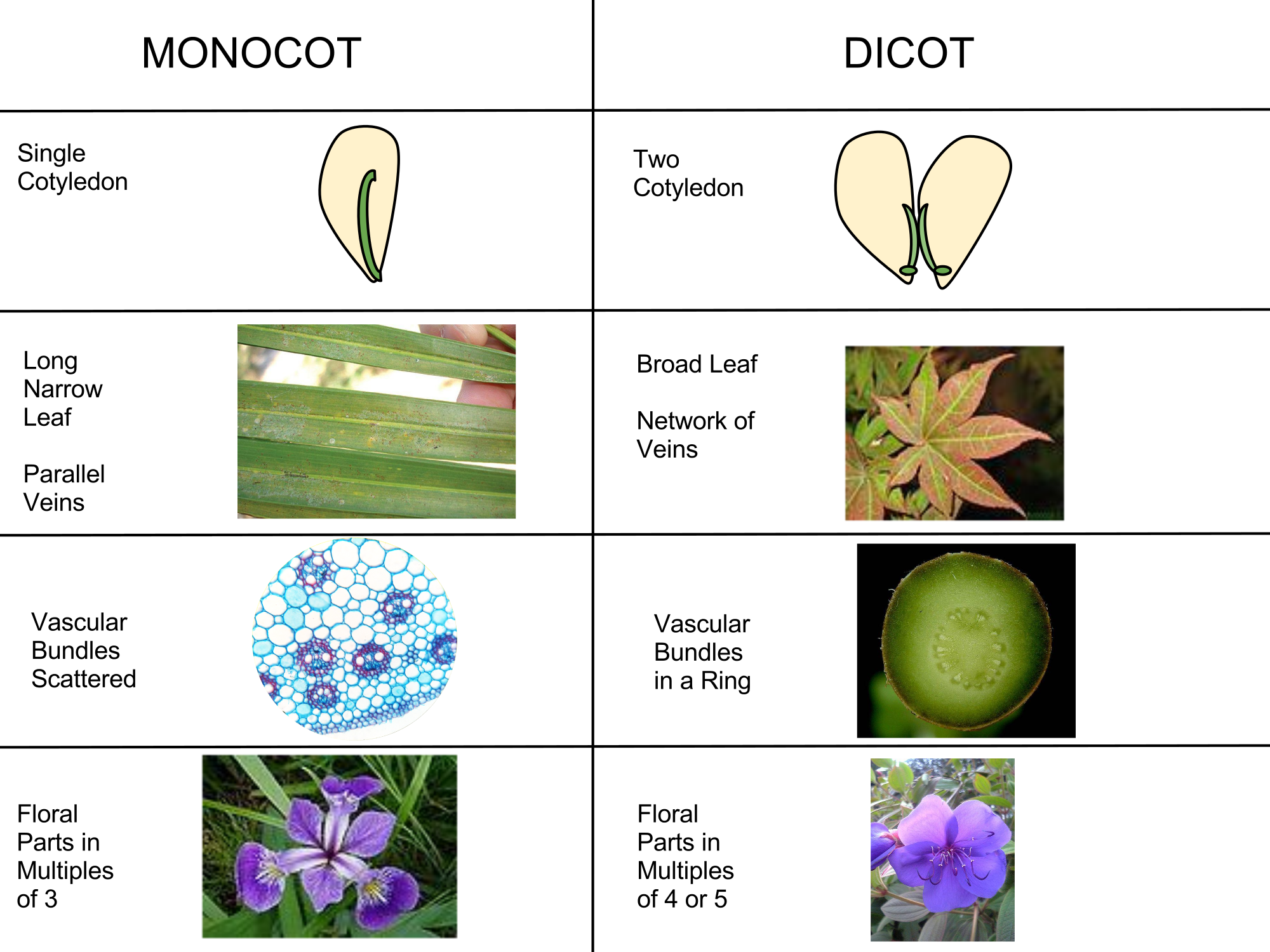
Monocot and dicot leaves contain similar types of dermal, ground, and vascular tissues, but they are arranged differently within each type of leaf.
How to draw monocot leaf. Leaves with parallel veining are grasses, tulips, irises, orchids, palms, corn, and bamboo. Web monocot leaves tend to have parallel venation, as opposed to the branching patterns seen in eudicots. The monocots are basically defined by their trimerous bauplan, regulating the structure of the flower as well as its evolution.
Grass examples of dicot leaves 1. Monocot leaves are isobilateral because the colour on both surfaces of the leaves is the same. Begin by making an outline of the main shape of the leaf.
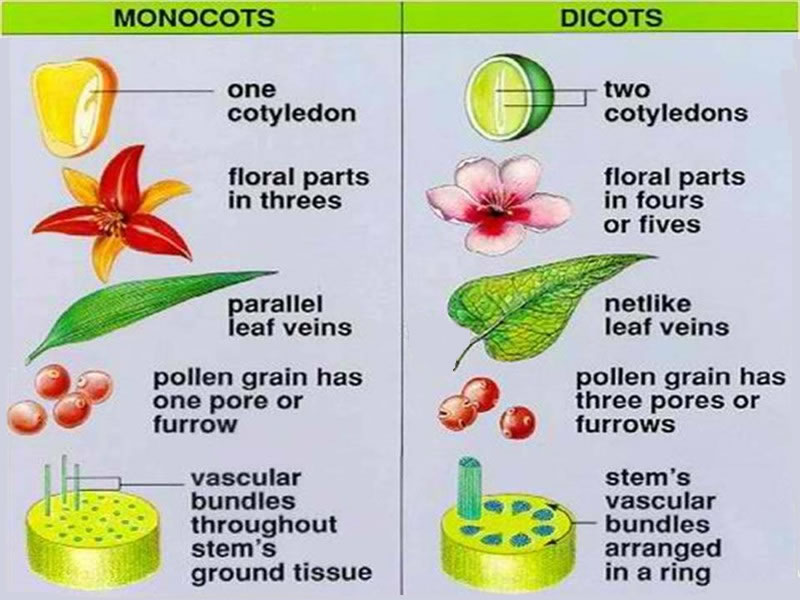
Two epidermal layers are present, one each on upper and lower surfaces. Monocots have parallel venation, while dicots have reticulate venation. Vascular bundles functions of monocot and dicot leaves monocot vs dicot leaves (13 key differences) examples of monocot leaves 1.
Web monocot leafzea mays leafhow to draw monocot leaf Make this narrower towards the base and wider towards the middle ending with a pointy tip. Web monocotyledon plant germination.it is really easy to distinguish a monocot from a dicot.
The leaves of flowering plants have an upper and lower surface, with the upper surface generally facing away from the ground and the lower surface facing toward it. Web draw and label cross sections of dicot and monocot leaves. The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called the venation pattern;
For example, monocots have leaf veins that form a parallel patter and flower parts in multiples of threes. Dicot leaves (dicotyledons) have net veining, also known as branching veins. Usually monocot plants have leaves with parallel venation.



















