Li, na, k, v, cr, fe, rb, nb, mo, cs, ba, ta, w, fr, ra, db, sg, ds, rg, eu:
How to draw face centered cubic structure of diamond. Web this demonstration lets you visualize and explore four different cubic crystal lattices: It is one of the most common structures for metals. Web diamond cubic crystal structure.
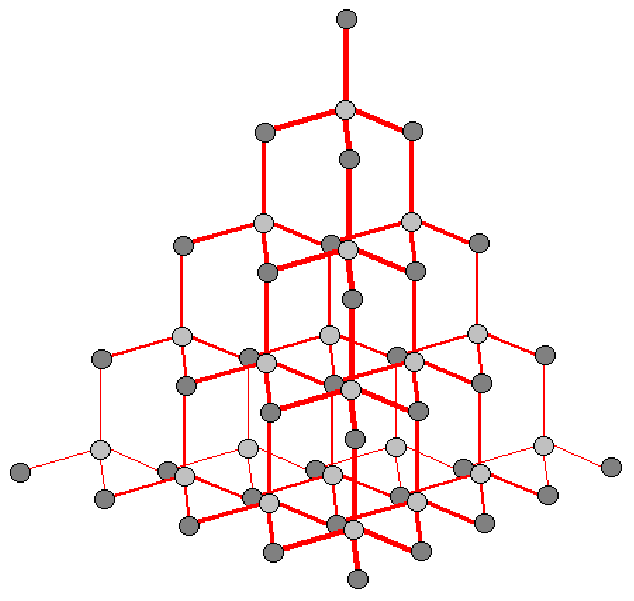
Note that the diamond structure is not a bravais The crystalline structure is of cubic symmetry with unit cell dimension pm, containing eight carbon atoms per unit cell. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright.
She also has prominent cheekbones and a prominent chin, therefore in this makeup tutoria. • tetrahedral and octahedral sites / vo. Web this video will show you how to draw different diagrams of the diamond in different perspective.
Web for all of you who didn't guess right, mia has a diamond face shape. Both graphite and diamond are crystalline forms of carbon. In diamonds, the atoms are very closely packed.
Web welcome to the world of material scienceface centered cubic crystal structure using mathematical animation1. There are 8 atoms per unit cell, and each atom is tetrahedrally coordinated so that it has 4 nearest neighbors. Web to build the diamond cubic, start with a cubical lattice, with an atom at each corner of each cube.
Web as also shown in figure 6.14.1, to describe the diamond structure, we first define the face centered cubic (fcc) lattice. It may also be described as face centered cubic lattice in which half of the tetrahedral sites are filled while all the octahedral sites remain vacant. A lattice of 3 × 3 × 3 unit cells.

















