Deadweight loss refers to the cost borne by society when there is an imbalance between the demand and supply.
How to calculate deadweight loss on a graph. Once you've learned how to calculate the areas of consumer and producer surplus on a graph when the market is in equilibrium, the next question is how so we. It is a market inefficiency that is caused by the. The deadweight loss equals the.
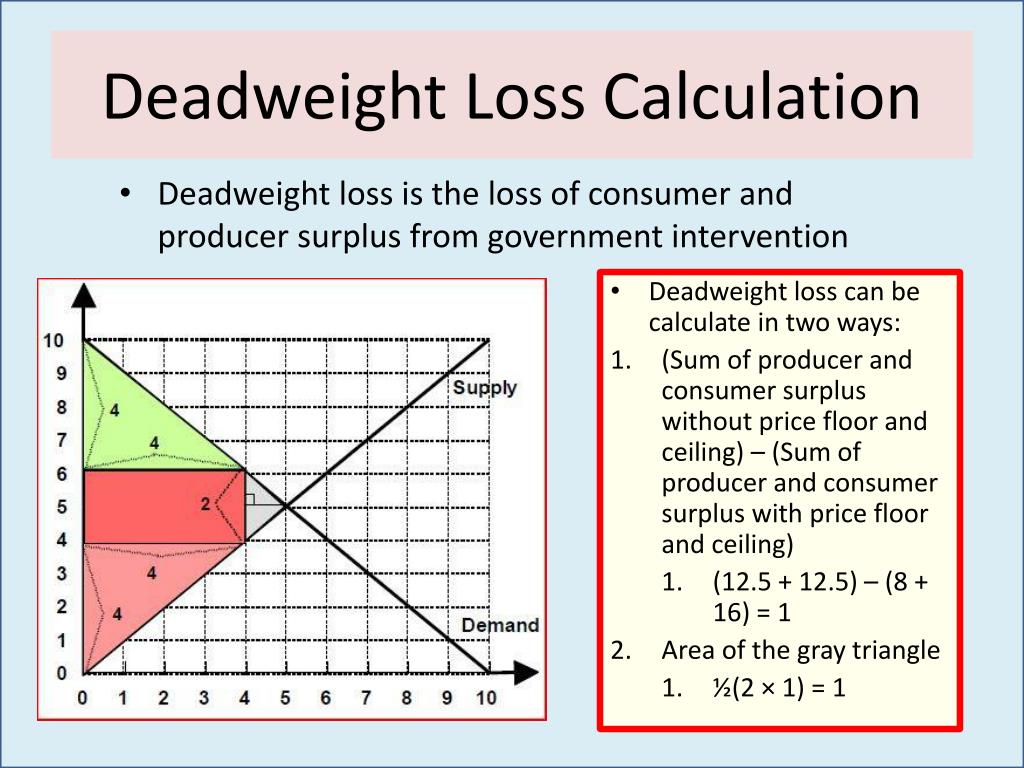
A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market. The difference between supply and demand curve (with the tax imposed) at q1 is 2. How to calculate deadweight loss.
Let’s first look at a graph representing the problem. Firstly, plot graph for the supply curve and the initial demand curve with a price on the ordinate and quantity on the abscissa. So the base of our deadweight loss triangle will be 1.
Learn how to calculate deadweight loss using the deadweight loss formula & deadweight loss graph. This means that our q1 is 4, and our q2 is 5. For information on deadweight loss look here.
The original price of the product in question (p o)the new price for the. How do you calculate deadweight loss on a monopoly graph? A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market.
In order to determine the deadweight loss in a market, the equation p=mc is used. So in this example, deadweight is $20 minus $15 or $5. Now we use the equation for finding the area of a triangle to calculate this.









