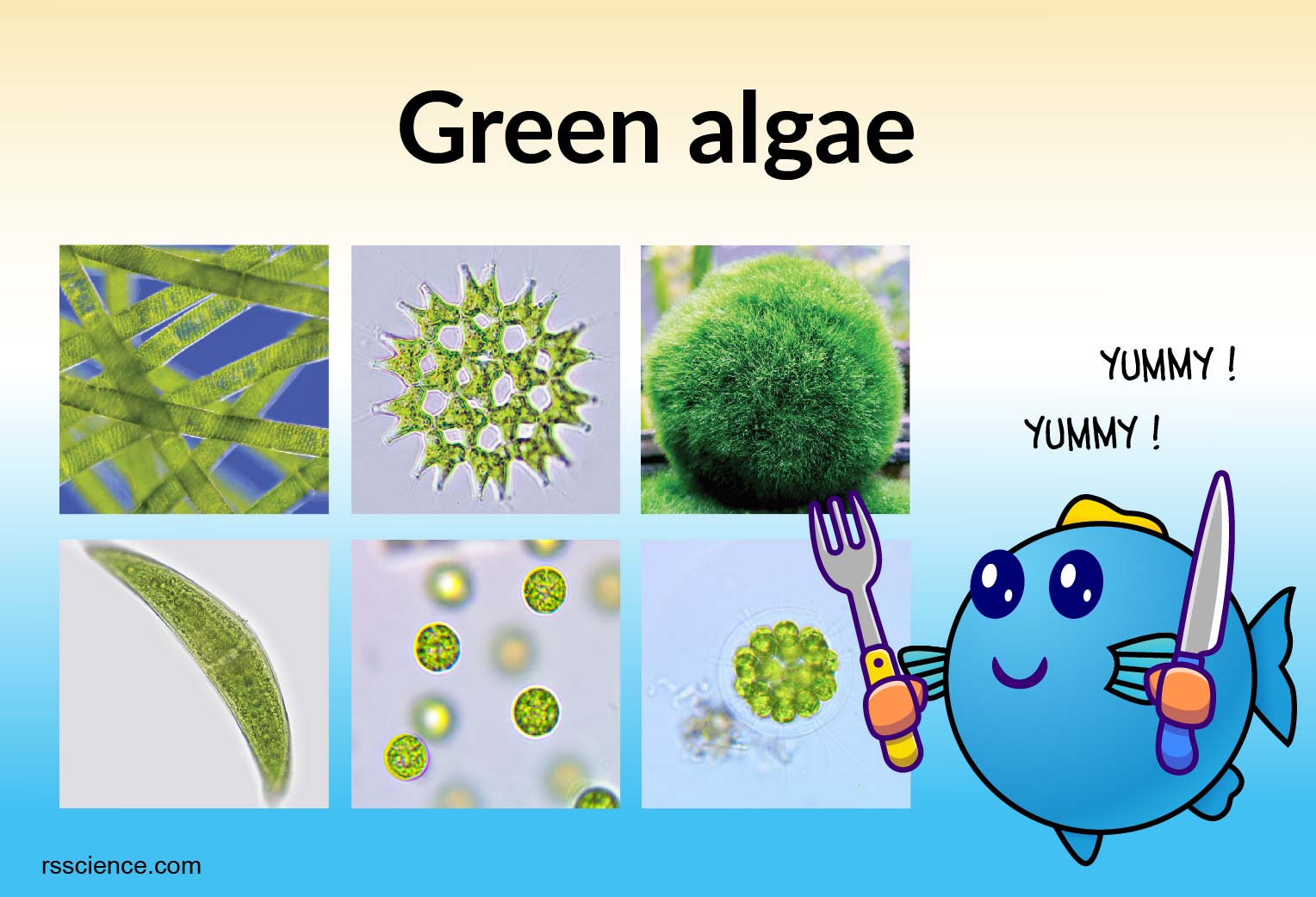
Web green algae, members of the division chlorophyta, comprising between 9,000 and 12,000 species.
Green algae are unicellular or multicellular. Web classification and taxonomy algae belong to a paraphyletic group that is distinguished from the other groups of organisms. Web higher organisms use green algae to conduct photosynthesis for them. Wehr, in freshwater algae of north america, 2003 c.
Unicellular unicellular species will have two whiplash flagella. Web chlamydomonas is a small (unicellular</strong> , mobile organism. Many unicellular species form colonies.
Web complex multicellular organisms, not counting the aggregation of amoebae to form slime molds, have evolved within only six eukaryotic lineages:. Green algae chlorophyta or green algae. The unicellular green algae species engage in.
These organisms are found in the supergroups. Web the multicellular volvocine species volvox carteri exhibits many hallmarks of complex multicellularity. Carteri provide a unique opportunity to study multicellularity and cellular differentiation at.
Web introduction living organisms are unicellular, composed of a single cell, or multicellular, where a group of up to ~10 12 cells functions co. Many have sheaths to bind other cells or filaments. Web the streptophytes (charophyte algae + embryophytes [land plants]) and their sister group, the chlorophytes (green algae),.
Web cyanobacteria may be unicellular or filamentous. Web similar to red algae, green algae can be unicellular or multicellular. It is roughly spherical in shape with two.











