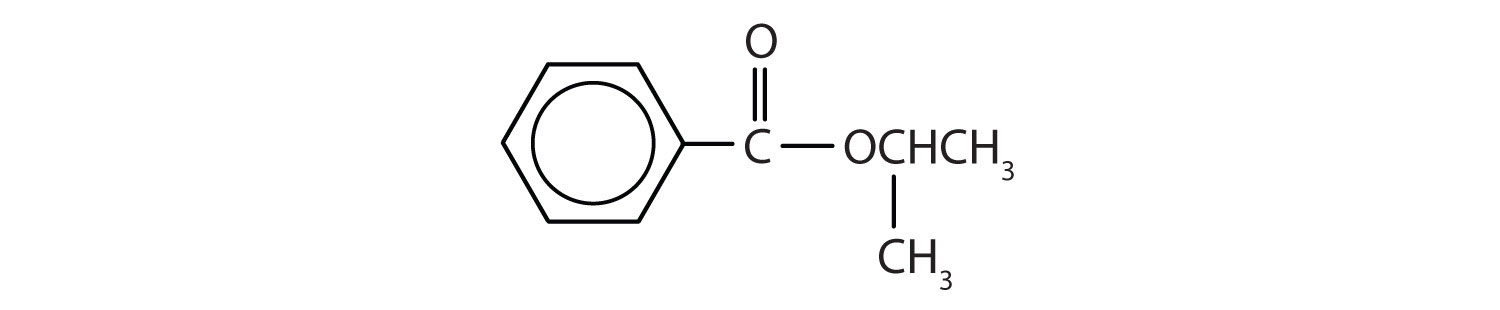
The suffix for an ester is -oate.
Ester name examples. An esterification reaction involves a molecule of carboxylic acid with a molecule of alcohol in the presence of a strong acid catalyst such as concentrated sulphuric acid to form an ester and water. Esters feature a carbon-to-oxygen double bond that is also singly bonded to a second oxygen atom which is then joined to an alkyl or an aryl group. 47 rows In chemistry an ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid organic.
The part enclosed by the red circle represents the ethyl group from the alcohol and the part enclosed by the green rectangle represents the acetate group from the acid. The good is that esters follow the same pattern and instead of the metal ion we use the alkyl group connected to the RCO acyl fragment. For example the ester formed by ethanol and ethanoic acid is known as ethyl ethanoate.
Unlike carboxylic acids esters generally have pleasant odors and are often responsible for the characteristic fragrances of fruits and flowers. An example of this is the reaction of acetic acid with an alcohol which yields an acetic ester and water. Naming Esters - Chemistry Steps.
Ethanol is reduced to ethyl while ethanoic acid is reduced to ethanoate Other examples of ester names include methyl propanoate from methanol and propanoic acid and. The esterification process of ethanol and butanoic acid to ethyl butanoate and water. Esters occur widely in nature.
For example sodium acetate potassium butyrate etc. 7 rows How to name esters. The carboxylic acid portion is named as if it were deprotonated ie.
The esters shown here are ethyl acetate a and methyl butyrate b. In the IUPAC nomenclature of carboxylic acids we learned that their salts are named by replacing the suffix ic acid or oic acid with ate. The names for carboxylic acid and ester compounds are derived using similar nomenclature rules as seen previously with aldehydes and include the class-identifying suffixes -oic acid and -oate respectively.

.bmp?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=434&height=321)







