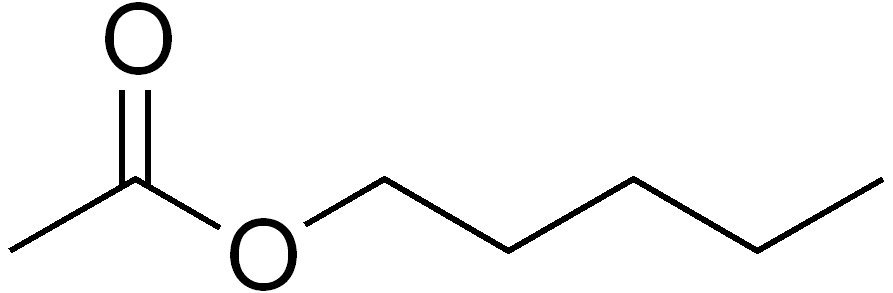
Name of the ester.
Ester name ethanoate. A carbonyl carbon bonded to two carbon atoms distinguishes ketones from carboxylic acids aldehydes esters amides and other oxygen containing compounds. Notice that the ester is named the opposite way around from the way the formula is written. Since the CO came from the parent acid there were four carbon atoms in the acid molecule butanoic acid and.
The formula for ethyl ethanoate is. In this case the hydrogen in the COOH group has been replaced by an ethyl group. The two organic radicals which are often carbon chains labelled R 1 and R 2 in the diagram at the top of this page are also identified in the name of the compound.
In this case the hydrogen in the -COOH group has been replaced by an ethyl group. Benzenecarboxylic acid Benzoic acid 1-chloromethyl ethanoate. An alkyl group in green is attached directly to the oxygen atom by its middle carbon atom.
I have colour-coded the structure and name to show how they are related. Notice that the ester is named the opposite way around from the way the formula is written. First the alcohol part is named and then followed by the acid part.
The most commonly discussed ester is ethyl ethanoate. In the molecule below the ester link -COO separates the two parts of the molecule. The formula for ethyl ethanoate is.
The standard system for naming esters uses the suffix -oate to indicate that a molecule is an ester. 2 Nomenclature of esters The name of an ester contains the names of The alkyl group from the alcohol. Organic chemistry The acetate anion C2H3O2 a carboxylate and the conjugate base of ethanoic acid acetic acid.









