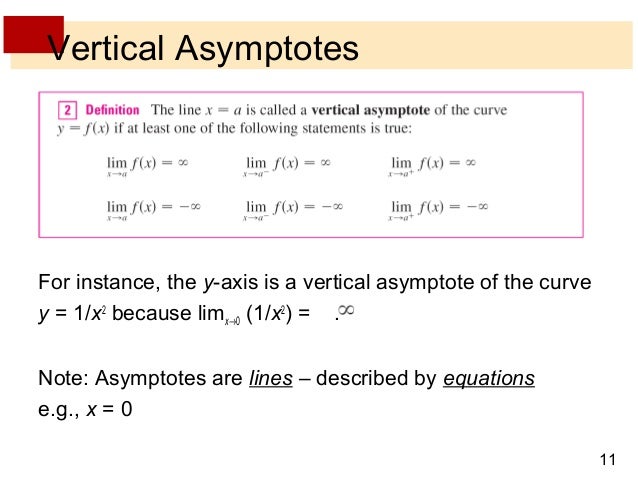
Vertical asymptote defines the domain of a function.
Definition vertical asymptote. They are vertical lines drawn in lightly or. Asymptote in geometry, a line associated with a curve in such a way that the distance between. You can see that from.
A vertical asymptote is an area of a graph where the function is undefined. Vertical asymptotes occur when a factor of the denominator of a rational expression does not cancel with a factor from the numerator. When you have a factor that does not cancel,.
To recap, a vertical asymptote is an invisible line which the graph never touches. Degree of denominator = 2. A horizontal asymptote occurs when a function of x approaches some constant, c (from the left or right) then the curve continues to infinity (or −infinity).
The distance between asymptote and graph. Vertical asymptote when x approaches some constant value c from left. What is a vertical asymptote in calculus?
As x approaches some constant value c (from the left or right) then the curve goes towards infinity (or −infinity). Since the degree of the numerator is smaller than that of the denominator, the horizontal asymptote is given by: Vertical asymptote rules when the graph gets closer to the vertical asymptote, it tends to negative/ positive infinity.
The vertical asymptote is a place where the function is undefined and the limit of the function does not exist. This is because as 1 approaches the. Vertical asymptotes are straight lines of the equation , toward which a function f ( x) approaches infinitesimally closely, but never reaches the line, as f ( x) increases without bound.









