It can visually be portrayed what effects it has on consumer and producer surpluses and how that relates to.
Deadweight loss on a graph. Please keep in mind that these. In economics, deadweight loss is the difference in production and consumption of any given product or service including government tax. My 60 second explanation of how to identify the consumer and producer surplus on the monopoly graph.
Mainly used in economics, deadweight loss. If a good has a negative externality, then the cost to society is negative externality graph dead weight loss in. A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market.
A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market. A deadweight loss is a cost to society created by market inefficiency, which occurs when supply and demand are out of equilibrium. This would shift the supply curve to the left and cause a deadweight loss.
Notice that monopolies charge a higher price and produce. It is a market inefficiency that is caused by the. The deadweight loss calculator helps you understand and calculate the economic cost to society when cournot dead weight loss on graph factors impact market prices.
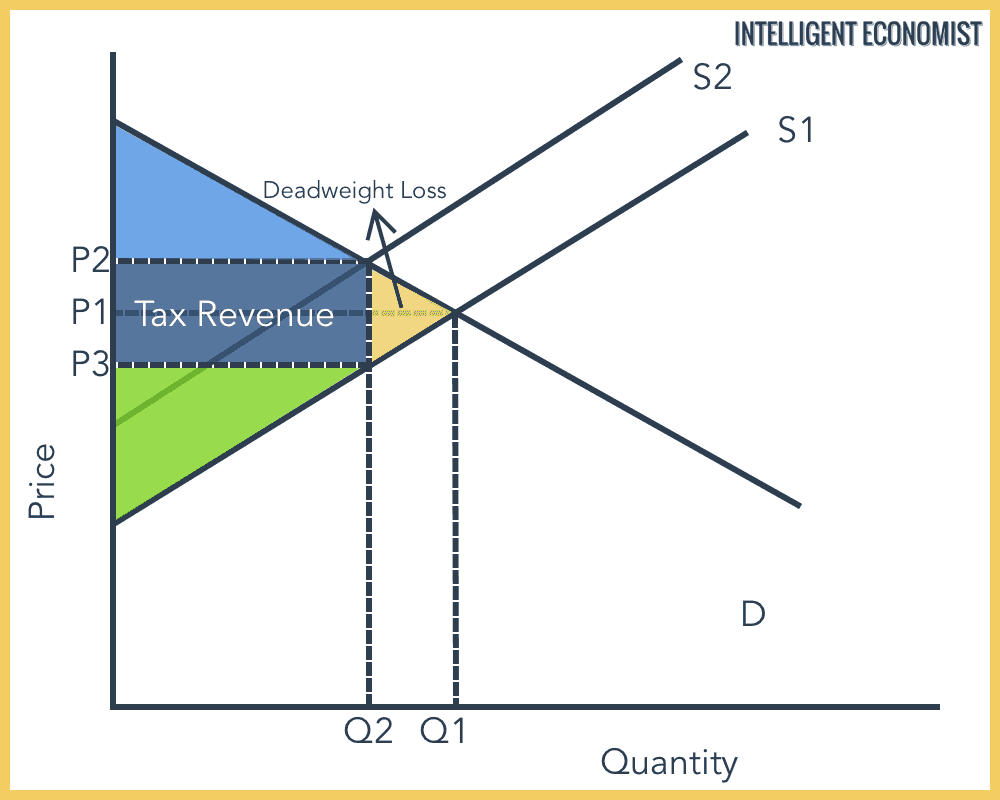
Deadweight loss refers to the cost borne by society when there is an imbalance between the demand and supply. Before i go through the associated math, let’s first look at a graph representing the problem. Deadweight loss graph using the minimum wage example;
In the deadweight loss graph below, the deadweight loss is represented by the area of the blue triangle, which is equal to the price difference (base of the triangle) multiplied by the quantity. In the graph, the equilibrium point is denoted by f and the quantity by ob. Shows the deadweight loss (as measured on a.









