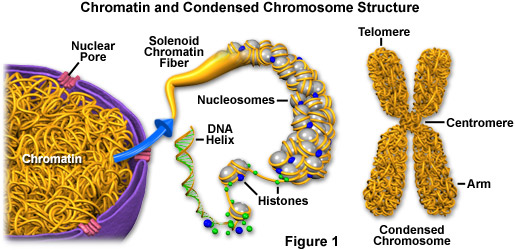
Chromatin, chromosome, and chromatid chromatin is composed of dna and histones that are packaged into thin, stringy fibers.
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes. The packaging of chromatin into chromosomes enable the efficient splitting of the genetic material during cell division, which in turn ensures that each daughter cell receives their own. During prophase chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the nuclear envelope (the membrane surrounding the nucleus) breaks down. What causes chromatin to condense?
Specific histone modifications, e.g., histone h1 and h3 phosphorylation,. In animal cells the centrioles near the. Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein found in eukaryotic cells.
In prophase, the chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes. See answers (2) best answer. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and prophase i in meiosis.
The nucleosome is made up of eight proteins called histones. During prophase, the complex of dna and proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses. What happens when chromatin condenses into chromosomes?
[1] the primary function is to package long dna molecules into more compact, denser structures. Structure that contains identical dna copies and is formed during dna replication. What chromatin condenses into chromosomes?
The nucleosomes loop themselves into a 30 nm spiral to produce a solenoid. What causes chromatin to condense? Nucleosomes are the name for these beads.