Usually this ballast is in form of a weighted fin often with a bulb attached to the bottom.
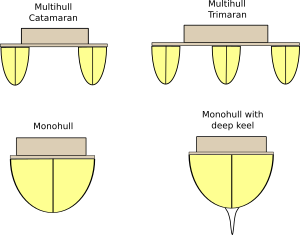
Catamaran ship stability. 2 Area A₂ is to be not less than 003 mrad. The reasons are more than obvious. In order to keep a monohull upright she will need ballast which will resist the heeling force of the wind.
It is great for liveaboard space and comfort at the dock but taken to extremes it will produce an uncomfort-able motion in a seaway. The metacentric height is an approximation for the vessel stability at a small angle 0-15 degrees of heel. This book differs from the rest in the sense that the content is not presented as discrete topics unrelated to each other.
5 θmax is to be. Passenger catamarans completely satisfy requirements regarding space and stability as well as other functional needs of the users. This boat has a particularly wide beam which makes for more stability and more space.
In addition a narrower hull is more easily depressed and prone to tripping in heavy seas. The catamaran due to its light displacement and great initial stability will likely perform well in moderate conditions and will heel very little but it has essentially no reserve stability to rely on when conditions get extreme. Most books however are difficult to follow due to the unsystematic way the materials are presented.
The Voyage 44 is a South African-made catamaran with a rugged design considered a cost-effective option with superior sailing performance relative to other ships sold at the same price point. Ship must comply with. Origin of Catamarans The catamaran was first created by the fishing community Paravas in Tamil Nadu in the 17 th century.
She did drown a few passengers on her upper decks though in the course of distinguishing herself as the only vessel in history to knock over a water tower with her wheelhouse really. Sadly multitudes of precious. The main feature of these boats was the fact that they had two hulls which offered a lot of stability and balance as compared to the other fishing boats of that era.



















