Catamaran Boat Plans PDF: Your Guide to Building Your Dream Vessel
So, you’re dreaming of sailing the open seas, feeling the wind in your hair, and exploring hidden coves? Sounds fantastic, right? But instead of buying a pre-made catamaran, you’re thinking about building your own. That’s a bold and rewarding adventure! And if you’re looking for a starting point, you’ve probably stumbled upon the phrase “catamaran boat plans PDF.” Let’s dive into what that really means and how you can use these resources to make your nautical dreams a reality.
First things first, what exactly is a “catamaran boat plans PDF”? Simply put, it’s a digital blueprint for constructing a catamaran. These plans are usually delivered in PDF format, making them easy to download and access from any device. You’ll find detailed instructions, measurements, and diagrams that guide you through every step of the building process. These plans are crucial for anyone considering a DIY catamaran project.
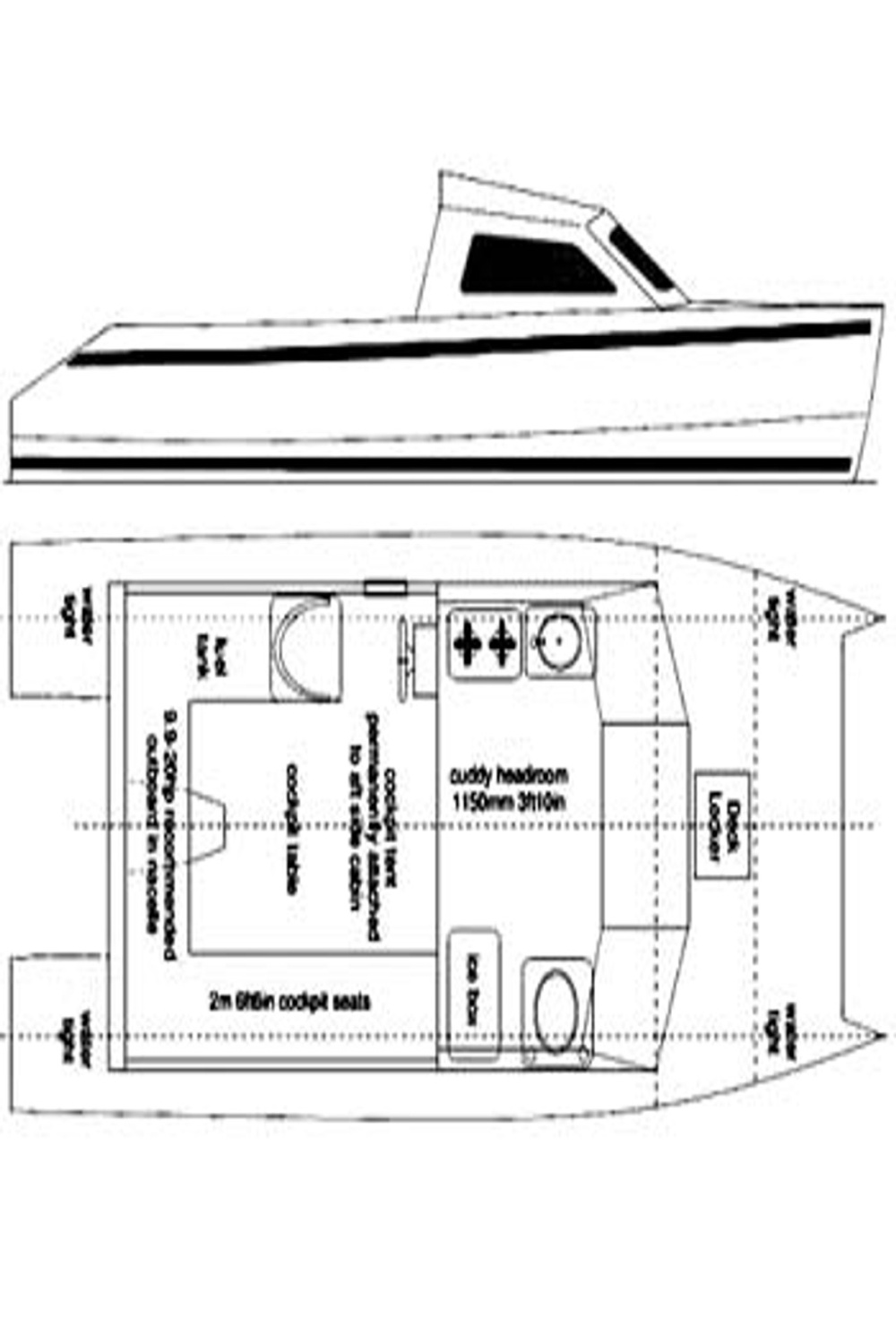
Why choose a catamaran, anyway? Well, they’re known for their stability, spaciousness, and shallow draft. These qualities make them perfect for cruising, fishing, or even living aboard. And building one yourself? That’s a whole other level of satisfaction. You’ll have a vessel that’s uniquely yours, tailored to your specific needs and preferences. Plus, using a “catamaran boat plans PDF” can save you a ton of money compared to buying a new or used catamaran.
Finding the right “catamaran boat plans PDF” is key. You’ll want to look for plans that are:
Detailed and Comprehensive: Clear instructions and accurate measurements are essential. You don’t want to be left guessing halfway through the build.
Once you’ve found the perfect “catamaran boat plans PDF,” it’s time to gather your materials. You’ll need wood, fiberglass, resin, and various hardware. The exact materials will depend on the design of your catamaran. And remember, quality materials are crucial for a safe and durable vessel.
Building a catamaran is a significant undertaking. It requires time, patience, and a good amount of skill. But with the right “catamaran boat plans PDF” and a can-do attitude, you can create a beautiful and functional vessel. Don’t be afraid to ask for help from experienced boat builders or online communities. There are plenty of resources available to guide you along the way.
One of the best things about using a “catamaran boat plans PDF” is the flexibility it offers. You can customize the design to suit your specific needs. Want a larger cabin? No problem. Need a different layout? You got it. You’re the captain of this ship, literally!
Remember, safety should always be your top priority. Ensure that your catamaran meets all safety regulations and standards. And before you set sail, make sure you have all the necessary safety equipment on board.
The digital format of the “catamaran boat plans PDF” allows you to print the plans out as needed. This can be very useful when you have certain sections that you are working on, and don’t want to risk damaging your computer or tablet. It also allows you to make your own notes on the printed pages.
When you’re searching for “catamaran boat plans PDF” online, take the time to read reviews and testimonials from other boat builders. This can give you valuable insights into the quality and usability of the plans. You may also find that some designers offer support and assistance during the build, which can be invaluable.
The process of building your own catamaran is a journey of discovery. You’ll learn new skills, overcome challenges, and experience the satisfaction of creating something truly unique. And when you finally launch your catamaran, you’ll feel a sense of accomplishment that’s hard to match.
In conclusion, using a “catamaran boat plans PDF” is an excellent way to build your own catamaran. It offers flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and the satisfaction of creating a vessel that’s uniquely yours. With careful planning, quality materials, and a bit of elbow grease, you can turn your nautical dreams into reality. So, download those plans, gather your tools, and set sail on your building adventure!
FAQs
Where can I find reliable catamaran boat plans PDF files?
You can find them from reputable online boat design companies, experienced naval architects, and some online forums specializing in DIY boat building. Always check reviews and testimonials before purchasing.
What skill level is required to build a catamaran from a PDF plan?
It varies. Some plans are designed for beginners, while others require advanced boat building skills. Carefully assess your own abilities and choose plans that match your skill level.
What materials do I need to build a catamaran?
Common materials include marine-grade plywood, fiberglass, epoxy resin, and various hardware. The specific materials will depend on the design of the catamaran. The “catamaran boat plans PDF” will list all needed materials.
Can I customize the catamaran boat plans PDF design?
Yes, one of the advantages of using PDF plans is the flexibility they offer. You can often make modifications to the design to suit your specific needs and preferences.
How long does it take to build a catamaran from PDF plans?
The time it takes to build a catamaran can vary widely, depending on the size and complexity of the design, as well as your skill level and available time. It can range from several months to a few years.