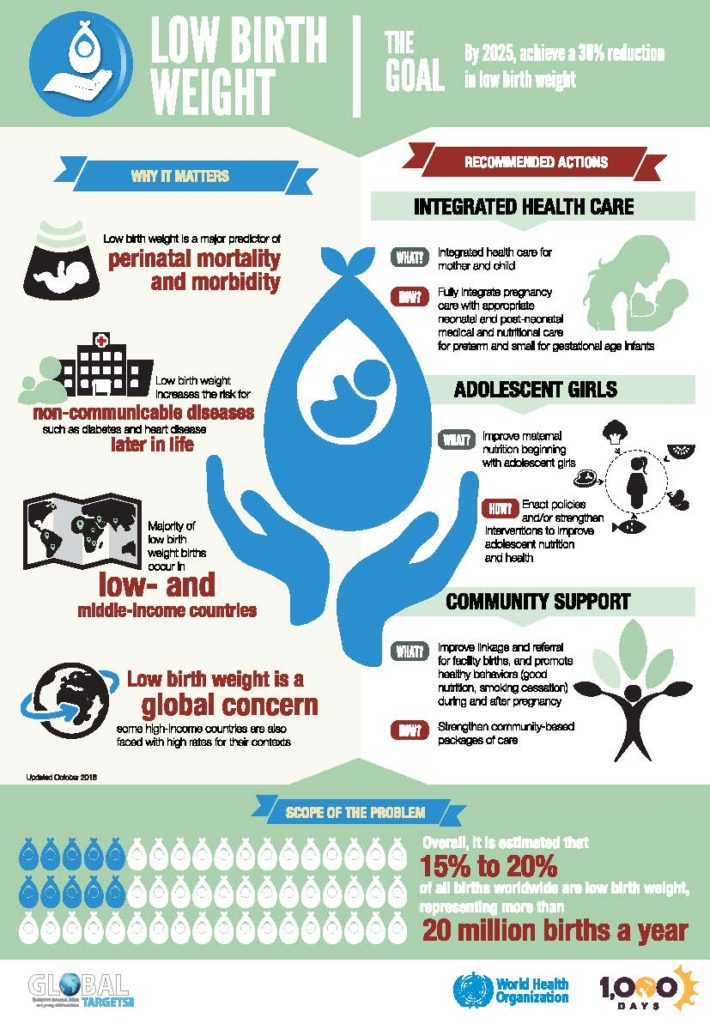
Low birth weight (LBW) defined a birth weight less 2500 (up and including 2499 g), per World Health Organization (WHO) [1]. definition LBW been existence many decades.
 Low birth weight a preventable public health problem. is important determinant child survival development, well long-term consequences the onset non-communicable disease the life course. large number mortality .
Low birth weight a preventable public health problem. is important determinant child survival development, well long-term consequences the onset non-communicable disease the life course. large number mortality .


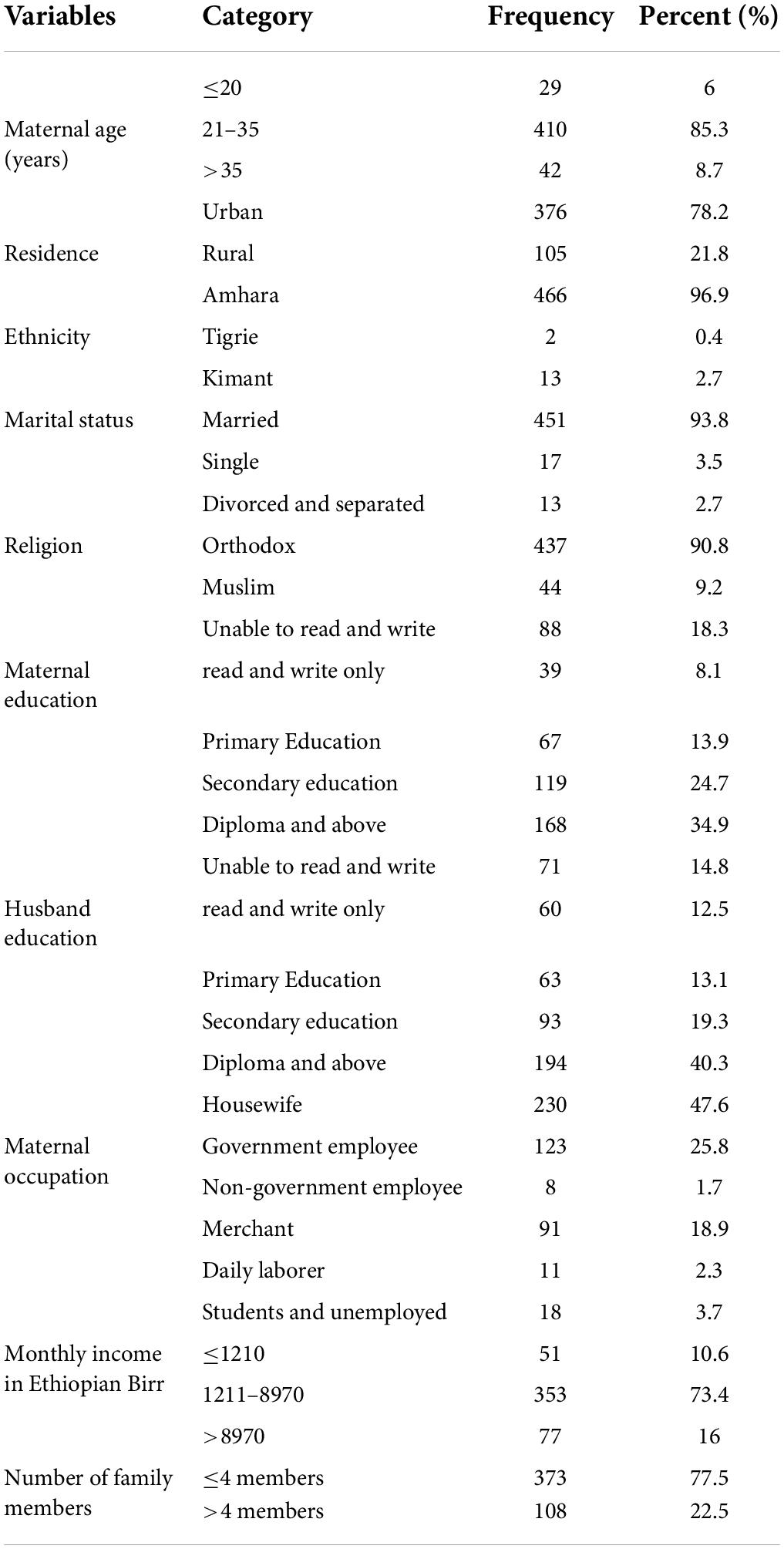
 Background this umbrella review, systematically evaluated evidence meta-analyses systematic reviews maternal factors with low birth weight. Methods PubMed, Scopus, Web Science searched identify relevant published studies to August 2023. included meta-analysis studies (based cohort, case-control, cross-sectional studies) .
Background this umbrella review, systematically evaluated evidence meta-analyses systematic reviews maternal factors with low birth weight. Methods PubMed, Scopus, Web Science searched identify relevant published studies to August 2023. included meta-analysis studies (based cohort, case-control, cross-sectional studies) .
 Birth weight a critical indicator assessing foetal development newborn health status [1]. Abnormal birth weights linked various adverse outcomes including low birth weight, macrosomia, being small (SGA) large (LGA) gestational age, well preterm birth. conditions only impact children's and long-term health, manifesting stunted growth .
Birth weight a critical indicator assessing foetal development newborn health status [1]. Abnormal birth weights linked various adverse outcomes including low birth weight, macrosomia, being small (SGA) large (LGA) gestational age, well preterm birth. conditions only impact children's and long-term health, manifesting stunted growth .

 Objectives. compare associations socioeconomic status low birth weight the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, countries share cultural features differ terms public support health care systems.Methods. .
Objectives. compare associations socioeconomic status low birth weight the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, countries share cultural features differ terms public support health care systems.Methods. .
 Low birth weight more common developing developed countries. However, data low birth weight developing countries often limited a significant portion deliveries occur homes small health facilities, cases infants low birth weight go unreported.
Low birth weight more common developing developed countries. However, data low birth weight developing countries often limited a significant portion deliveries occur homes small health facilities, cases infants low birth weight go unreported.
 Although reliable data the magnitude global distribution low birth weight (LBW, birth weight <2,500 grams) remain limited (de Onis al., 1998a), World Health Organization estimates more 20 million LBW infants born year, affecting approximately 16 percent all newborns developing countries. LBW an important risk factor neonatal postneonatal .
Although reliable data the magnitude global distribution low birth weight (LBW, birth weight <2,500 grams) remain limited (de Onis al., 1998a), World Health Organization estimates more 20 million LBW infants born year, affecting approximately 16 percent all newborns developing countries. LBW an important risk factor neonatal postneonatal .
 Prenatal and birth characteristics of very low birth weight (VLBW
Prenatal and birth characteristics of very low birth weight (VLBW
 (PDF) Prevalence of low birth weight in India and its determinants
(PDF) Prevalence of low birth weight in India and its determinants
 Causes of low birth weight in babies | Best Gynecologists in Bangalore
Causes of low birth weight in babies | Best Gynecologists in Bangalore
 Classification of live low birth weight babies | Download Scientific
Classification of live low birth weight babies | Download Scientific
 Low Birth Weight in Babies - Causes, Facts, Factors And More - Being
Low Birth Weight in Babies - Causes, Facts, Factors And More - Being
 Prevalence of low birth weight and preterm delivery | Download
Prevalence of low birth weight and preterm delivery | Download
 Low Birth Weight | Birth Injury Law Firm
Low Birth Weight | Birth Injury Law Firm
 How To Prevent Low Birth Weight During Pregnancy - PregnancyWalls
How To Prevent Low Birth Weight During Pregnancy - PregnancyWalls
 8% of US babies born in 2015 had low birth weight, compared with 75%
8% of US babies born in 2015 had low birth weight, compared with 75%
 New study identifies risk factors associated with low birth weight
New study identifies risk factors associated with low birth weight
 (PDF) Preterm and Low Birth Weight Babies
(PDF) Preterm and Low Birth Weight Babies