The membrane surface facing the lumen is called the apical surface, and the membrane surface on the side facing blood is called the basolateral surface.
Apical surface. Apical surface in oxford dictionary of biochemistry and molecular biology ». This is particularly evident in epithelial and endothelial cells , but also describes. We find that many radial nanometer bristles, referred to as nanobristles, project from the lateral surface of nematode and mouse microvilli.
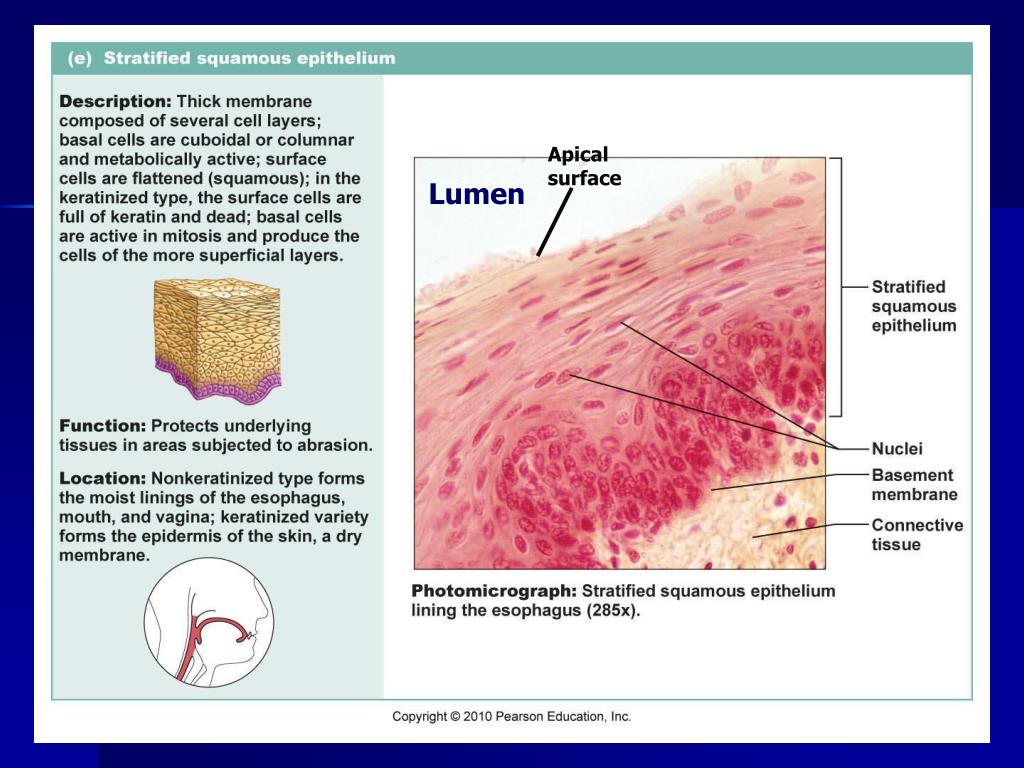
The apical membrane of a polarized cell is the surface of the plasma membrane that faces inward to the lumen. The cells on the apical surface contain multiple projections on their plasma membrane made of microtubules called microvilli d. The surface of an epithelial cell that faces the lumen.
Cell lineages derived from the apical cell will progressively differentiate to form cotyledons, shoot meristem, hypocotyl axis, and embryonic root (figure 4).by contrast, the basal cell will divide. All the cells share an apical surface c. Elegans nanobristles are 37.5 nm long and.
Of, at, or being the apex | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples We find that many radial nanometer bristles referred to as nanobristles project from the lateral surface of nematode and mouse microvilli. An apical surface is a surface that faces the lumen which is the inner cavity of an organ.
Translocation to the surface is activated by pka (protein. The apical surface of the epithelial cell is the upper free surface exposed to the body exterior or the cavity of an internal organ, the structural. Present in alveoli, fallopian tubes and ejaculatory ducts.
An organ of structure also has a basal side which faces the basement membrane and is commonly in. Owing to the shape of the cells, the primary functions of the simple cuboidal epithelium are secretion, absorption, and covering. The cells on the apical surface contain.









