The basolateral surface which is opposite to the apical surface and faces the basement membrane.
Apical and basal surfaces. What is the apical and basal surface of a cell? In other words, it is the most superficial layer of the epithelium. The terms apical cell and basal cell are used to describe the relative locations within stratified epithelium.
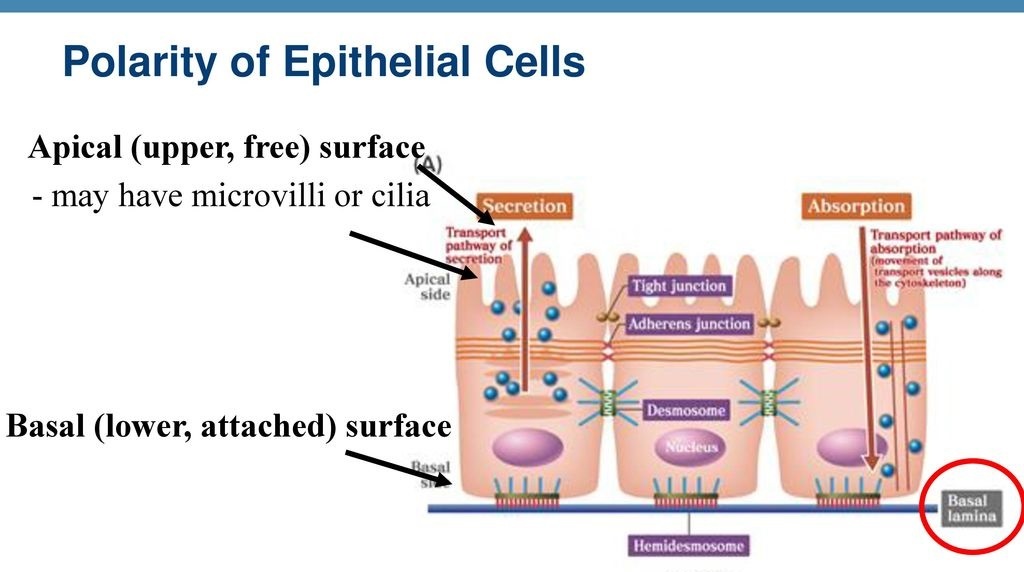
The various surfaces of epithelium have different names, including 'apical', 'lateral', and 'basal', and each plays a different functional role. The apical surface is exposed at the surface of the body or the lumen of the body cavity, ducts, tubes, or vessels. Epithelia cells are polarized with an apical surface that faces the lumen of a tube or the external environment and a basal surface.
Epithelial tissue is a membranous tissue made up of cells that form various surfaces and linings throughout the body. The apical and basal surfaces perform different functions and have unique biochemical compositions. Epithelia are polarized, with an apical surface that faces the external environment and a basal surface that faces the basement membrane.
The apical surface faces the lumen (inside of a hollow organ) while the basal or basolateral surface is adjacent to the underlying tissue. Hemadsorption and virus budding occurred on the apical surface but were not apparent on the basal surface of monolayers 1 and 5 h after inversion, although cellular ha antigen. What is a basement membrane?
Cellularization occurs in an apical to basal direction, as membranes grow basally from the surface of the embryo to surround each nucleus of the syncytium (fig. Epithelial cells are continuously renewed. Basement membranes are thin layers.
This means, the apical surface. Although most epithelial tissues are a type of tissue on the surface of. In many epithelia the apical surface.









